- Компании
- Takeda. О компании, буклеты, каталоги, контакты
- Olympus. О компании, буклеты, каталоги, контакты
- Boston Scientific. О компании, буклеты, каталоги, контакты
- Pentax. О компании, буклеты, каталоги, контакты
- Fujifilm & R-Farm. О компании, буклеты, каталоги, контакты
- Erbe. О компании, буклеты, каталоги, контакты
- Еще каталоги
- Мероприятия
- Информация
- Обучение
- Классификации
- Атлас
- Quiz
- Разделы
- Пациенту
QR-код этой страницы
Для продолжения изучения на мобильном устройстве ПРОСКАНИРУЙТЕ QR-код с помощью спец. программы или фотокамеры мобильного устройства
Случайный выбор
данная функция, случайным образом выбирает информацию для Вашего изучения,
запустите выбор нажав кнопку ниже
Обратная связь
Напишите нам
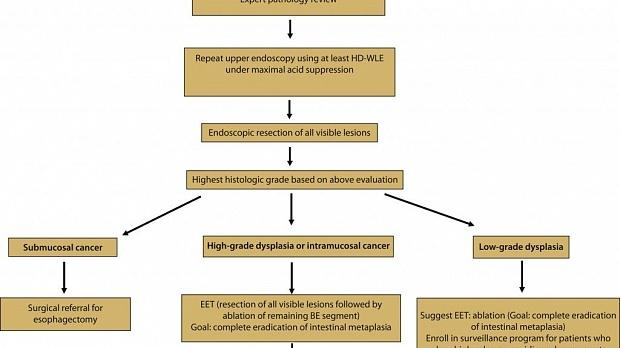
Новости: Рекомендации по эндоскопическому лечению пациентов с дисплазией и внутрислизистым раком при пищеводе Баррета.
Полный текст статьи:
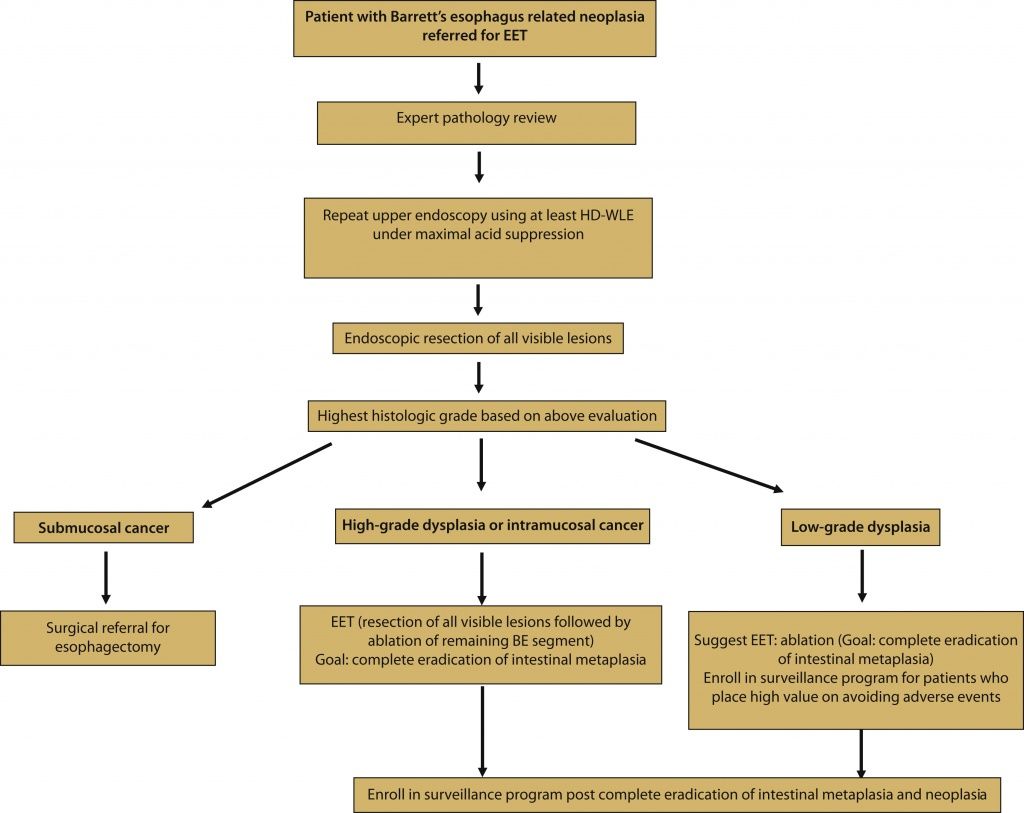
Американское общество гастроинтестинальной эндоскопии предлагает ознакомиться с новыми рекомендациями по эндоскопическому лечению пациентов с дисплазией и внутрислизистым раком при пищеводе Баррета.
Пищевод барретта (BE) определяется заменой нормального плоскоклеточного эпителия дистального пищевода метапластическим столбчатым эпителием кишечного типа.
Читать полный текст абстракта статьи...
Endoscopic eradication therapy for patients with Barrett’s esophagus–associated dysplasia and intramucosal cancer
Prepared by: Standards of Practice Committee, Sachin Wani, MD∗; Bashar Qumseya, MD, MPH∗; Shahnaz Sultan, MD; Deepak Agrawal, MD; Vinay Chandrasekhara, MD; Ben Harnke, PhD; Shivangi Kothari, MD; Martin McCarter, MD; Aasma Shaukat, MD, MPH; Amy Wang, MD; Julie Yang, MD; John Dewitt, MD
Abstract
Barrett’s esophagus (BE) is defined by the replacement of the normal squamous epithelium of the distal esophagus with metaplastic intestinal-type columnar epithelium.1-3 BE is an adverse event of chronic GERD and the only identifiable premalignant condition for esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC), a cancer that continues to increase in incidence. In 2014 there were approximately 18,170 incident cases of esophageal cancer in the United States, nearly 60% of which were EAC.4-6 Although uncommon, EAC is a highly lethal cancer associated with a poor 5-year survival rate of 15% to 20% and an overall median survival of <1 year in cases with advanced disease.
Источник:
References
• American Gastroenterological Association, Spechler, S.J., Sharma, P., Souza, R.F. et al. American Gastroenterological Association medical position statement on the management of Barrett's esophagus. Gastroenterology. 2011; 140: 1084–1091
• Shaheen, N.J., Falk, G.W., Iyer, P.G. et al. ACG clinical guideline: diagnosis and management of Barrett's esophagus. (quiz 51)Am J Gastroenterol. 2016; 111: 30–50
• Wani, S., Rubenstein, J.H., Vieth, M. et al. Diagnosis and management of low-grade dysplasia in Barrett's esophagus: expert review from the Clinical Practice Updates Committee of the American Gastroenterological Association. Gastroenterology. 2016; 151: 822–835
• Rubenstein, J.H. and Shaheen, N.J. Epidemiology, diagnosis, and management of esophageal adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2015; 149: 302–317
• Hur, C., Miller, M., Kong, C.Y. et al. Trends in esophageal adenocarcinoma incidence and mortality. Cancer. 2013; 119: 1149–1158
• Pohl, H. and Welch, H.G. The role of overdiagnosis and reclassification in the marked increase of esophageal adenocarcinoma incidence. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005; 97: 142–146
• Lepage, C., Rachet, B., Jooste, V. et al. Continuing rapid increase in esophageal adenocarcinoma in England and Wales. Am J Gastroenterol. 2008; 103: 2694–2699
• Ronkainen, J., Aro, P., Storskrubb, T. et al. Prevalence of Barrett's esophagus in the general population: an endoscopic study. Gastroenterology. 2005; 129: 1825–1831
• Zagari, R.M., Fuccio, L., Wallander, M.A. et al. Gastro-oesophageal reflux symptoms, oesophagitis and Barrett's oesophagus in the general population: the Loiano-Monghidoro study. Gut. 2008; 57: 1354–1359
• Wani, S., Falk, G., Hall, M. et al. Patients with nondysplastic Barrett's esophagus have low risks for developing dysplasia or esophageal adenocarcinoma. (quiz e226)Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011; 9: 220–227
• Wani, S., Falk, G.W., Post, J. et al. Risk factors for progression of low-grade dysplasia in patients with Barrett's esophagus. Gastroenterology. 2011; 141: 1179–1186
• Rastogi, A., Puli, S., El-Serag, H.B. et al. Incidence of esophageal adenocarcinoma in patients with Barrett's esophagus and high-grade dysplasia: a meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2008; 67: 394–398
• Hvid-Jensen, F., Pedersen, L., Drewes, A.M. et al. Incidence of adenocarcinoma among patients with Barrett's esophagus. N Engl J Med. 2011; 365: 1375–1383
• Wani, S., Muthusamy, V.R., Shaheen, N.J. et al. Development of quality indicators for endoscopic eradication therapies in Barrett's esophagus: the TREAT-BE (Treatment with Resection and Endoscopic Ablation Techniques for Barrett's Esophagus) Consortium. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017; 86: 1–17
• Wani, S. and Sharma, P. Challenges with endoscopic therapy for Barrett's esophagus. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2015; 44: 355–372
• Shaheen, N.J., Sharma, P., Overholt, B.F. et al. Radiofrequency ablation in Barrett's esophagus with dysplasia. N Engl J Med. 2009; 360: 2277–2288
• Phoa, K.N., van Vilsteren, F.G., Weusten, B.L. et al. Radiofrequency ablation vs endoscopic surveillance for patients with Barrett esophagus and low-grade dysplasia: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2014; 311: 1209–1217
• Wolf, W.A., Pasricha, S., Cotton, C. et al. Incidence of esophageal adenocarcinoma and causes of mortality after radiofrequency ablation of Barrett's esophagus. Gastroenterology. 2015; 149: 1752–1761
• Pech, O., Behrens, A., May, A. et al. Long-term results and risk factor analysis for recurrence after curative endoscopic therapy in 349 patients with high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia and mucosal adenocarcinoma in Barrett's oesophagus. Gut. 2008; 57: 1200–1206
• Orman, E.S., Li, N., and Shaheen, N.J. Efficacy and durability of radiofrequency ablation for Barrett's esophagus: systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013; 11: 1245–1255
• Phoa, K.N., Pouw, R.E., van Vilsteren, F.G. et al. Remission of Barrett's esophagus with early neoplasia 5 years after radiofrequency ablation with endoscopic resection: a Netherlands cohort study. Gastroenterology. 2013; 145: 96–104
• Qumseya, B.J., Wani, S., Desai, M. et al. adverse events after radiofrequency ablation in patients with Barrett's esophagus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016; 14: 1086–
• Wani, S., Drahos, J., Cook, M.B. et al. Comparison of endoscopic therapies and surgical resection in patients with early esophageal cancer: a population-based study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2014; 79: 224–232
• Sultan, S., Falck-Ytter, Y., and Inadomi, J.M. The AGA institute process for developing clinical practice guidelines part one: grading the evidence. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013; 11: 329–332
• Moher, D., Liberati, A., Tetzlaff, J. et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med. 2009; 151: 264–269
• Shea, B.J., Grimshaw, J.M., Wells, G.A. et al. Development of AMSTAR: a measurement tool to assess the methodological quality of systematic reviews. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2007; 7: 10
• Yachimski, P., Wani, S., Givens, T. et al. Preference of endoscopic ablation over medical prevention of esophageal adenocarcinoma by patients with Barrett's esophagus. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015; 13: 84–90
• Hur, C., Wittenberg, E., Nishioka, N.S. et al. Patient preferences for the management of high-grade dysplasia in Barrett's esophagus. Dig Dis Sci. 2005; 50: 116–125
• Rosmolen, W.D., Boer, K.R., de Leeuw, R.J. et al. Quality of life and fear of cancer recurrence after endoscopic and surgical treatment for early neoplasia in Barrett's esophagus. Endoscopy. 2010; 42: 525–531
• Hur, C., Choi, S.E., Rubenstein, J.H. et al. The cost effectiveness of radiofrequency ablation for Barrett's esophagus. Gastroenterology. 2012; 143: 567–575
• Phoa, K.N., Rosmolen, W.D., Weusten, B.L. et al. The cost-effectiveness of radiofrequency ablation for Barrett's esophagus with low-grade dysplasia: results from a randomized controlled trial (SURF-trial). Gastrointest Endosc. 2017; 86: 120–129
• Pohl, H., Sonnenberg, A., Strobel, S. et al. Endoscopic versus surgical therapy for early cancer in Barrett's esophagus: a decision analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 70: 623–631
• Qumseya, B.J., Wani, S., Gendy, S. et al. Disease progression in Barrett's low-grade dysplasia with radiofrequency ablation compared with surveillance: systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2017; 112: 849–865
• Duits, L.C., van der Wel, M.J., Cotton, C.C. et al. Patients with Barrett’s esophagus and confirmed persistent low-grade dysplasia are at increased risk for progression to neoplasia. Gastroenterology. 2017; 152: 993–1001
• Schlemper, R.J., Riddell, R.H., Kato, Y. et al. The Vienna classification of gastrointestinal epithelial neoplasia. Gut. 2000; 47: 251–255
• Bosman, F., Carneiro, F., Hruban, R.H. et al. WHO classification of gastrointestinal tumors. IARC, Lyon, France; 2010
• Montgomery, E., Bronner, M.P., Goldblum, J.R. et al. Reproducibility of the diagnosis of dysplasia in Barrett esophagus: a reaffirmation. Hum Pathol. 2001; 32: 368–378
• Wani, S., Mathur, S.C., Curvers, W.L. et al. Greater interobserver agreement by endoscopic mucosal resection than biopsy samples in Barrett's dysplasia. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010; 8: 783–788
• Curvers, W.L., ten Kate, F.J., Krishnadath, K.K. et al. Low-grade dysplasia in Barrett's esophagus: overdiagnosed and underestimated. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010; 105: 1523–1530
• Vennalaganti, P., Kanakadandi, V., Goldblum, J.R. et al. Discordance among pathologists in the United States and Europe in diagnosis of low-grade dysplasia for patients with Barrett's esophagus. Gastroenterology. 2017; 152: 564–570
• Wani, S., Muthusamy, V.R., Shaheen, N.J. et al. Development of quality indicators for endoscopic eradication therapies in Barrett's esophagus: the TREAT-BE (Treatment with Resection and Endoscopic Ablation Techniques for Barrett's Esophagus) Consortium. Am J Gastroenterol. 2017; 112: 1032–1048
• Small, A.J., Araujo, J.L., Leggett, C.L. et al. Radiofrequency ablation is associated with decreased neoplastic progression in patients with Barrett's esophagus and confirmed low-grade dysplasia. Gastroenterology. 2015; 149: 567–576.e3
• Kestens, C., Offerhaus, G.J., van Baal, J.W. et al. Patients with Barrett's esophagus and persistent low-grade dysplasia have an increased risk for high-grade dysplasia and cancer. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016; 14: 956–962
• Tavakkoli, A., Appelman, H., Beer, D. et al. Risk factors for progression of Barrett's esophagus with low-grade dysplasia. Gastroenterology. 2016; 150: S177
• Overholt, B.F., Lightdale, C.J., Wang, K.K. et al. Photodynamic therapy with porfimer sodium for ablation of high-grade dysplasia in Barrett's esophagus: international, partially blinded, randomized phase III trial. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005; 62: 488–498
• Wu, J., Pan, Y.M., Wang, T.T. et al. Endotherapy versus surgery for early neoplasia in Barrett's esophagus: a meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2014; 79: 233–241
• Schmidt, M., Bodnar, A., Irani, S. et al. Multidisciplinary treatment of T1a adenocarcinoma in Barrett's esophagus: contemporary comparison of endoscopic and surgical treatment. ([abstract])Gastrointest Endosc. 2014; 79: AB495
• Wani, S., Early, D., Edmundowicz, S. et al. Management of high-grade dysplasia and intramucosal adenocarcinoma in Barrett's esophagus. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012; 10: 704–711
• Bennett, C., Vakil, N., Bergman, J. et al. Consensus statements for management of Barrett's dysplasia and early-stage esophageal adenocarcinoma, based on a Delphi process. Gastroenterology. 2012; 143: 336–346
• Dunbar, K.B. and Spechler, S.J. The risk of lymph-node metastases in patients with high-grade dysplasia or intramucosal carcinoma in Barrett's esophagus: a systematic review. (quiz 863)Am J Gastroenterol. 2012; 107: 850–862
• Fujii-Lau, L.L., Cinnor, B., Shaheen, N.J. et al. Recurrence of intestinal metaplasia and early neoplasia after endoscopic eradication therapy for Barrett's esophagus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Endosc Int Open. 2017; 05: E1–E20
• Krishnamoorthi, R., Singh, S., Ragunathan, K. et al. Risk of recurrence of Barrett's esophagus after successful endoscopic therapy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016; 83: 1090–1106
• Pasricha, S., Bulsiewicz, W.J., Hathorn, K.E. et al. Durability and predictors of successful radiofrequency ablation for Barrett's esophagus. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014; 12: 1840–1847
• Komanduri, S., Kahrilas, P.J., Krishnan, K. et al. Recurrence of Barrett's esophagus is rare following endoscopic eradication therapy coupled with effective reflux control. Am J Gastroenterol. 2017; 112: 556–566
• Leers, J.M., DeMeester, S.R., Oezcelik, A. et al. The prevalence of lymph node metastases in patients with T1 esophageal adenocarcinoma a retrospective review of esophagectomy specimens. Ann Surg. 2011; 253: 271–278
• Tomizawa, Y., Iyer, P.G., Wong Kee Song, L.M. et al. Safety of endoscopic mucosal resection for Barrett's esophagus. (quiz 1448)Am J Gastroenterol. 2013; 108: 1440–1447
• Pech, O., May, A., Manner, H. et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of endoscopic resection for patients with mucosal adenocarcinoma of the esophagus. Gastroenterology. 2014; 146: 652–660
• Wani, S., Abrams, J., Edmundowicz, S.A. et al. Endoscopic mucosal resection results in change of histologic diagnosis in Barrett's esophagus patients with visible and flat neoplasia: a multicenter cohort study. Dig Dis Sci. 2013; 58: 1703–1709
• Wani, S., Sayana, H., and Sharma, P. Endoscopic eradication of Barrett's esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 71: 147–166
• Mino-Kenudson, M., Hull, M.J., Brown, I. et al. EMR for Barrett's esophagus-related superficial neoplasms offers better diagnostic reproducibility than mucosal biopsy. (quiz 767, 769)Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 66: 660–666
• Sharma, P., Katzka, D.A., Gupta, N. et al. Quality indicators for the management of Barrett's esophagus, dysplasia, and esophageal adenocarcinoma: international consensus recommendations from the American Gastroenterological Association Symposium. Gastroenterology. 2015; 149: 1599–1606
• Manner, H., Rabenstein, T., Pech, O. et al. Ablation of residual Barrett's epithelium after endoscopic resection: a randomized long-term follow-up study of argon plasma coagulation vs. surveillance (APE study). Endoscopy. 2014; 46: 6–12
• Desai, M., Saligram, S., Gupta, N. et al. Efficacy and safety outcomes of multimodal endoscopic eradication therapy in Barrett's esophagus-related neoplasia: a systematic review and pooled analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017; 85: 482–495
• Anders, M., Bahr, C., El-Masry, M.A. et al. Long-term recurrence of neoplasia and Barrett's epithelium after complete endoscopic resection. Gut. 2014; 63: 1535–1543
• Small, A.J., Sutherland, S.E., Hightower, J.S. et al. Comparative risk of recurrence of dysplasia and carcinoma after endoluminal eradication therapy of high-grade dysplasia versus intramucosal carcinoma in Barrett's esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015; 81: 1158–1166
• Vaccaro, B.J., Gonzalez, S., Poneros, J.M. et al. Detection of intestinal metaplasia after successful eradication of Barrett's Esophagus with radiofrequency ablation. Dig Dis Sci. 2011; 56: 1996–2000
• Cotton, C.C., Wolf, W.A., Pasricha, S. et al. Recurrent intestinal metaplasia after radiofrequency ablation for Barrett's esophagus: endoscopic findings and anatomic location. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015; 81: 1362–1369
• Pasricha, S., Cotton, C., Hathorn, K.E. et al. Effects of the learning curve on efficacy of radiofrequency ablation for Barrett's esophagus. Gastroenterology. 2015; 149: 890–896
• van Vilsteren, F.G., Pouw, R.E., Herrero, L.A. et al. Learning to perform endoscopic resection of esophageal neoplasia is associated with significant complications even within a structured training program. Endoscopy. 2012; 44: 4–12
• Fudman, D.I., Lightdale, C.J., Poneros, J.M. et al. Positive correlation between endoscopist radiofrequency ablation volume and response rates in Barrett's esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc. 2014; 80: 71–77
Рекомендуемые статьи
При эндоскопическом исследовании в случае бронхоэктазов в стадии ремиссии выявляется
частично диффузный бронхит I степени воспаления
Работаем и учимся при поддержке
Партнеры

Вы находитесь в разделе предназначенном только для специалистов (раздел для пациентов по ссылке). Пожалуйста, внимательно прочитайте полные условия использования и подтвердите, что Вы являетесь медицинским или фармацевтическим работником или студентом медицинского образовательного учреждения и подтверждаете своё понимание и согласие с тем, что применение рецептурных препаратов, обращение за той или иной медицинской услугой, равно как и ее выполнение, использование медицинских изделий, выбор метода профилактики, диагностики, лечения, медицинской реабилитации, равно как и их применение, возможны только после предварительной консультации со специалистом. Мы используем файлы cookie, чтобы предложить Вам лучший опыт взаимодействия. Файлы cookie позволяют адаптировать веб-сайты к вашим интересам и предпочтениям.
Я прочитал и настоящим принимаю вышеизложенное, хочу продолжить ознакомление с размещенной на данном сайте информацией для специалистов.










.jpg)

.png)















Комментарии