- Компании
- Takeda. О компании, буклеты, каталоги, контакты
- Olympus. О компании, буклеты, каталоги, контакты
- Boston Scientific. О компании, буклеты, каталоги, контакты
- Pentax. О компании, буклеты, каталоги, контакты
- Fujifilm & R-Farm. О компании, буклеты, каталоги, контакты
- Erbe. О компании, буклеты, каталоги, контакты
- Еще каталоги
- Мероприятия
- Информация
- Обучение
- Классификации
- Атлас
- Quiz
- Разделы
- Пациенту
QR-код этой страницы

Для продолжения изучения на мобильном устройстве ПРОСКАНИРУЙТЕ QR-код с помощью спец. программы или фотокамеры мобильного устройства
Документы и приказы: Химический ожог пищевода. Клинические рекомендации 2021 - 2023
Полный текст статьи:
Химический ожог пищевода
классификации болезней и проблем, связанных со здоровьем:T28.6
- Общероссийская общественная организация "Российское общество хирургов"
- Региональная Общественная организация "Национальное общество Торакальных Хирургов"
- Межрегиональная благотворительная общественная организация "Ассоциация клинических токсикологов
Оглавление
- Список сокращений
- Термины и определения
- 1. Краткая информация по заболеванию или состоянию (группы заболеваний или состояний)
- 1.1 Определение заболевания или состояния (группы заболеваний или состояний)
- 1.2 Этиология и патогенез заболевания или состояния (группы заболеваний или состояний)
- 1.3 Эпидемиология заболевания или состояния (группы заболеваний или состояний)
- 1.4 Особенности кодирования заболевания или состояния (группы заболеваний или состояний) по Международной статической класификации болезней и проблем, связанных со здоровьем
- 1.5 Классификация заболевания или состояния (группы заболеваний или состояний)
- 1.6 Клиническая картина заболевания или состояния (группы заболеваний или состояний)
- 2. Диагностика заболевания или состояния (группы заболеваний или состояний) медицинские показания и противопоказания к применению методов диагностики
- 2.1 Жалобы и анамнез
- 2.2 Физикальное обследование
- 2.3 Лабораторные диагностические исследования
- 2.4 Инструментальные диагностические исследования
- 2.5 Иные диагностические исследования
- 3. Лечение, включая медикаментозную и немедикаментозную терапии, диетотерапию, обезболивание, медицинские показания и противопоказания к применению методов лечения
- 4. Медицинская реабилитация, медицинские показания и противопоказания к применению методов реабилитации
- 5. Профилактика и диспансерное наблюдение, медицинские показания и противопоказания к применению методов профилактики
- 6. Организация оказания медицинской помощи
- 7. Дополнительная информация (в том числе факторы, влияющие на исход заболевания или состояния)
- Критерии оценки качества медицинской помощи
- Список литературы
- Приложение А1. Состав рабочей группы по разработке и пересмотру клинических рекомендаций
- Приложение А2. Методология разработки клинических рекомендаций
- Приложение А3. Справочные материалы, включая соответствие показаний к применению и противопоказаний, способов применения и доз лекарственных препаратов, инструкции по применению лекарственного препарата
- Приложение Б. Алгоритмы действий врача
- Приложение В. Информация для пациента
- Приложение Г1-ГN. Шкалы оценки, вопросники и другие оценочные инструменты состояния пациента, приведенные в клинических рекомендациях
Список сокращений
АД – артериальное давление
АлАТ – аланинаминотрансфераза
АсАТ – аспартатаминотрансфераза
ВПД – вещества прижигающего действия
ДВС – диссеминированное внутрисосудистое свертывание
ЖКТ – желудочно-кишечный тракт
КТ – компьютерная томография
КЩС – кислотно-щелочное состояние
ЛДГ – лактатдегидрогеназа
РСП – рубцовое сужение пищевода
ЭГДС – эзофагогастродуоденоскопия
УЗИ – ультразвуковое исследование
ХОП – химический ожог пищевода
Термины и определения
Химический ожог пищевода – местное повреждение стенки пищевода вследствие случайного или преднамеренного приёма через рот химического вещества прижигающего действия
Вещества прижигающего действия – химические вещества или их смеси, вызывающие при контакте со слизистыми оболочками или кожными покровами химический ожог, сопровождающийся общетоксическими симптомами.
Отравление веществами прижигающего действия – системное заболевание, отдельная нозологическая форма ожоговой болезни химической этиологии.
Токсикант - более широкое понятие, чем яд, употребляющееся не только для обозначения веществ, вызвавших интоксикацию, но провоцирующих и другие формы токсического процесса, и не только организма, но и биологических систем иных уровней организации: клеток (цитотоксикант), популяций (экотоксикант).
Послеожоговая стриктура пищевода – сужение просвета пищевода различной протяженности и на разных его уровнях за счет разрастания и созревания рубцовой ткани в стенке пищевода вследствие воздействия экзогенных факторов, сопровождающиеся его деформацией.
1. Краткая информация по заболеванию или состоянию (группы заболеваний или состояний)
1.1 Определение заболевания или состояния (группы заболеваний или состояний)
Химический ожог пищевода - местное повреждение стенки пищевода вследствие случайного или преднамеренного приёма через рот химического вещества прижигающего действия (ВПД) [1,3,4,11,68].
Химический ожог пищевода сопровождается токсическим резорбтивным действием.
1.2 Этиология и патогенез заболевания или состояния (группы заболеваний или состояний)
Причиной химического ожога пищевода (ХОП) является случайный или преднамеренный приём через рот концентрированных растворов неорганических или органических кислот (азотной, серной, соляной, уксусной, щавелевой), растворов щелочей (едкого натра, едкого калия), а также сильных окислителей (перманганата калия, перекиси водорода, других окислителей, входящих в состав многочисленных современных моющих, чистящих, отбеливающих средств), аммиака, ацетона, йода [3,11,16,64 – 66,68].
В патогенезе химического ожога пищевода выделяют местные и общие патологические процессы [4,69].
Местные изменения
Глубина поражения тканей и распространенность ожога зависит от вида прижигающего вещества, его концентрации, количества (объёма в мл.) и времени контакта с тканями организма.
В клинико-морфологическом течении химических ожогов пищевода выделяют следующие стадии:
1) Стадия контакта прижигающего вещества со стенкой пищевода. Она длится от нескольких минут до момента оказания медицинской помощи.
При кратковременном контакте, малом количестве и слабой концентрации химического агента, а также при термическом ожоге, стадия контакта выражается в отеке и гиперемии слизистой оболочки полости рта, глотки и начальных отделов пищевода (I степень ожога).
2) Стадия ожогового флегмонозного или некротически-язвенного эзофагита. Длится от трех до шести суток. Эта стадия ожога возникает при более длительном контакте с химическим агентом и выражается в деструкции слизистой оболочки и подслизистого слоя (II степень ожога). Некоторые исследователи с учётом того, что при гибели подслизистого слоя исходом является образование рубцовой ткани, подразделяют эту степень ожога на IIа (поражение только слизистой оболочки) и на IIб (поражение слизистой оболочки и подслизистого слоя).
В этой стадии возникают так называемые ранние пищеводные кровотечения.
Некроз слизистой оболочки, подслизистого слоя и, частично, мышечной оболочки представляет собой III степень ожога. При этом концентрированные растворы кислот и окислители образуют плотный некротический струп (коагуляционный некроз) и сопровождаются обширными тромбозами сосудов стенки пищевода.
При действии концентрированных растворов щелочей возникает рыхлый (колликвационный) некротический слой с расплавлением тканей на большую глубину.
3) Стадия отторжения некротических тканей (от шести до десяти суток после ожога). Отторжение больших участков некротических тканей приводит к позднему пищеводному кровотечению, которое может иметь профузный характер и трудно поддается лечению.
При ожоге пищевода III степени в 18-30% наблюдений поражается и стенка желудка, но меньше, чем пищевод, так как при отравлении кислотой оказывается, что слизистая оболочка желудка более устойчива, чем слизистая оболочка пищевода, а при отравлении щёлочью часть её нейтрализуется кислым содержимым желудка.
Но при этом страдает замыкательная функция кардии и возникает рефлюкс-эзофагит, поддерживая длительное течение патологического процесса, особенно при сопутствующем ожоге антрального отдела с нарушением эвакуации из желудка.
Прием большого количества (более 100 мл) прижигающего раствора и длительная его экспозиция приводят к обширному поражению не только пищевода и желудка, но и двенадцатиперстной и тощей кишки и быстрой смерти от интоксикации (IV степень ожога). Морфологически пищевод при этом выглядит как распадающийся в руках тяж темно-багрового или черного цвета с перифокальным серозным медиастинитом, а при прижизненной перфорации – с гнойно-некротическим анаэробным медиастинитом.
Пораженная стенка желудка при ожоге IV степени имеет вид «папирусной бумаги» – истонченной ткани серого цвета с мутным выпотом в поддиафрагмальном пространстве.
В редких наблюдениях исходом ограниченного некроза пищевода может быть образование пищеводно-медиастинального или пищеводно-респираторного свища. Такой исход возможен при попадании в пищевод и фиксации в его стенке нерастворенных в принятой через рот жидкости единичных кристаллов перманганата калия.
4) Стадия развития грануляционной ткани и формирование рубцов (от шести суток до года). При ожоге III степени язвенная поверхность покрывается грануляционной тканью, которая частично замещается тонкой соединительной (рубцовой) тканью, что приводит к деформациям и сужениям просвета пищевода с нарушением его проходимости. Медленно текущий подострый воспалительный процесс стихает в сроки от одного до двух лет после ожога.
5) Стадия стойких рубцовых изменений. В зависимости от распространенности и глубины ожога – от единичных стриктур до многочисленных, а иногда до полной облитерации просвета.
Данные о частоте развития рубцовых послеожоговых стриктур пищевода разноречивы и колеблются от 8 до 73% от числа всех наблюдений ожога пищевода [1,3,4].
Длительно существующее выраженное сужение пищевода приводит к супрастенотическому расширению его просвета, при этом, чем дистальнее расположено сужение, тем более выражено супрастенотическое расширение.
Полная облитерация просвета пищевода приводит к образованию так называемого слепого мешка, в котором из-за застоя инфицированной слюны и пищевых масс поддерживается хронический эзофагит. Стенка пищевода становится рыхлой, истонченной и при приеме большого количества жидкости может наступить гидравлический разрыв пищевода в супрастенотическом отделе.
Длительно существующая на фоне хронического эзофагита рубцовая ткань, постоянно травмируемая слюной, пищевыми массами (при сохраненной частичной проходимости) через 15-20 лет может приводить к развитию лейкоплакии, дисплазии и в конечном итоге злокачественному перерождению (плоскоклеточному раку) вероятность развития которого более чем в 2 тысячи раз выше, чем среди людей, у которых не было ожога пищевода [5].
Общетоксическое (резорбтивное) действие токсикантов при химическом ожоге
Степень общетоксического действия зависит от длительности и скорости резорбции. Длительность резорбции органических и неорганических кислот колеблется от 30 минут до 6 часов, щелочей - от 30 минут до 2 часов. Скорость резорбции в свою очередь зависит от площади ожога (количества ВПД и глубины ожога (концентрации ВПД) [6,67,68].
Наиболее частым и тяжёлым следствием приема ВПД является развитие экзотоксического шока при приёме не менее 50 мл вещества. В его основе лежит гиповолемия, обусловленная нарушениями сосудистой проницаемости вследствие грубых расстройств в системе микроциркуляции. В результате стрессорного действия токсиканта на организм активизируется симпатоадреналовая система, что вызывает сужение артериол, повышается периферическое сопротивление и систолическое артериальное давление (компенсированная фаза шока).
В патогенезе токсического шока большую роль играет токсическая коагулопатия, более всего выраженная при отравлении уксусной кислотой. Это связано с гемолизом эритроцитов и коагуляционным эффектом гемолизатов. Кроме того, поступление в кровь тканевого тромбопластина из разрушенных тканей усиливает агрегацию тромбоцитов и образование фибрина.
Декомпенсированная фаза шока – наступает при истощении катехоламинов и параличе артериол, что приводит к накоплению недоокисленных продуктов метаболизма и декомпенсированному ацидозу. Возникает анаэробный метаболизм, нарастает гиповолемия на фоне гепатопатии, нефропатии и ДВС – синдрома. Создается порочный круг, который без лечения заканчивается смертью.
1.3 Эпидемиология заболевания или состояния (группы заболеваний или состояний)
Острые отравления ВПД в России распространены больше, чем в других странах и составляют 7–15% от всех пострадавших, госпитализированных в центры лечения острых отравлений [4].
По данным специализированных центров по лечению отравлений в России в 1996 году отравления ВПД среди всех отравлений составляли 12,2% в Москве, 13,6% – в Перми и Екатеринбурге, 16,6% – в Санкт-Петербурге, причем на долю уксусной эссенции приходилось 70-80% от всех отравлений данной группы [2].
Несмотря на значительные успехи в диагностике и лечении пациентов с отравлениями ВПД, примерно у 45% из них развиваются осложнения, являющиеся причиной инвалидизации, летальность остается высокой, достигающая 20-25% [6-8].
Наибольшему риску подвержены две возрастные группы: дети в возрасте 2–6 лет, которые непреднамеренно проглатывают бытовые чистящие средства и составляют до 80% случаев проглатывания ВПД, но обычно имеют легкие травмы; и взрослые в возрасте 30–40 лет, которые обычно употребляли сильнодействующие разъедающие вещества с суицидальными намерениями и поступали с серьезными, опасными для жизни травмами [23,70].
У подавляющего большинства мужчин и женщин, приём прижигающей жидкости носит непреднамеренный характер и происходит в состоянии алкогольного опьянения (85-87%), когда небрежное хранение ядовитых жидкостей приводит к ошибочному их употреблению в качестве спиртного. В таких случаях люди делают большие глотки этой жидкости, что приводит к обширным и тяжелым химическим ожогам не только пищевода, но и желудка.
У женщин в качестве причин приема прижигающих жидкостей преобладают суицидальные попытки. Чаще всего они наблюдаются у женщин молодого возраста и носят сезонный характер (весна и осень). У части пациентов сознание возможной смерти и характер жидкости вызывает страх. Первый глоток яда приводит к спазму пищевода, и прижигающая жидкость выплевывается изо рта. В таких случаях ожог ограничивается яркой, демонстративной картиной поражения губ, слизистых оболочек полости рта, глотки и начальных отделов пищевода.
Пациенты, решившиеся на серьезные суицидальные действия, принимают залпом большое количество, свыше 50 - 100 мл прижигающей жидкости, и у них возникают глубокие ожоги не только полости рта, глотки и пищевода, но и желудка, двенадцатиперстной и тощей кишки. Такие пациенты погибают в первые двое-трое суток от тяжелой общей интоксикации и обширных некрозов тканей [4,7,16].
1.4 Особенности кодирования заболевания или состояния (группы заболеваний или состояний) по Международной статической класификации болезней и проблем, связанных со здоровьем
Т28.6 Химический ожог пищевода
1.5 Классификация заболевания или состояния (группы заболеваний или состояний)
Классификация ожогов по глубине повреждения стенки пищевода [7, 26]:
I степень – повреждение поверхностного эпителия с его отслоением и образованием эрозий.
II степень – повреждение всей слизистой оболочки с образованием поверхностных язв.
III степень – повреждение слизистой оболочки и мышечного слоя с образованием глубоких язв.
IV степень – повреждение всех слоев пищевода с вовлечением окружающих тканей и соседних органов.
По протяженности повреждения:
Ограниченный (до 3 см) – чаще всего повреждается пищевод в местах его физиологических сужений.
Протяженный – поражение пищевода на протяжении более 3 см.
Тотальный – поражение всего пищевода.
По сочетанности повреждения верхних отделов ЖКТ:
Изолированный ожог пищевода.
Сочетанный ожог пищевода и желудка/двенадцатиперстной кишки.
По стадиям клинического течения:
Острая (токсикогенная) стадия.
Стадия отторжения некротических тканей.
Стадия формирования послеожоговых рубцовых изменений.
Отдаленные сроки после ожога пищевода.
КТ-классификация тяжести ожоговой травмы пищевода
КТ-классификация тяжести ожоговой травмы пищевода предполагает четыре степени повреждения:
I степень – отсутствует отек стенки пищевода.
II степень – отек стенки пищевода без вовлечения параэзофагеальных тканей.
III степень – отек стенки пищевода с инфильтрацией параэзофагеальной клетчатки с четкостью контуров структур и тканей.
IV степень – отек стенки пищевода с инфильтрацией параэзофагеальной клетчатки, размытость/нечеткость контуров тканей или ограниченное скопление жидкости вокруг пищевода или нисходящей аорты. Отсутствие накопления контрастного вещества в стенке пищевода при контрастном усилении.
Эндоскопическая классификация Волкова С.В. (1997), дополненная Песней-Просоловой Е.А. (2006) [7].
По глубине ожога:
I степень – катаральное поражение (отек и гиперемия слизистой оболочки).
II степень – эрозивное поражение (не выходящее за пределы собственной мышечной пластинки слизистой оболочки).
III степень – язвенное поражение слизистой оболочки и подслизистого слоя.
IV степень – язвенно-некротическое поражение (слизистого, подслизистого и мышечного слоев пищевода).
По распространенности ожога:
Очаговый (в пищеводе – распространяются на 1/2 стенки и захватывают не более 1/3 его длины; в желудке – локализуются только в одном анатомическом отделе и распространяются не более чем на 2 стенки).
Ограниченный (в пищеводе – захватывают все стенки, то есть являются циркулярными и распространяются не более чем на 1/2 его длины; в желудке – циркулярные и полуциркулярные, локализуются в одном анатомическом отделе);
Распространенный (в пищеводе – циркулярные, захватывают более половины пищевода; в желудке – распространяются на 2 и более анатомических отдела, могут быть циркулярными и полуциркулярными либо в виде множественных очагов по всем стенкам).
По локализации поражения с учетом анатомических отделов пищевода и желудка:
пищевод – нижняя, средняя и верхняя его трети
желудок – кардиальный, фундальный и антральный отделы и его тело.
Эндоскопическая классификация Zargar S.A.
В мировой клинической практике наибольшее распространение имеет эндоскопическая классификация Zargar S.A. [16,25,26], позволяющая прогнозировать развитие послеожоговой стриктуры [27].
0 степень Нет изменений слизистой оболочки
I степень Поверхностный отек и эритема слизистой оболочки
IIA степень Кровоизлияния, эрозии, волдыри, поверхностные язвы
IIB степень Глубокие дискретные и циркулярные язвы
IIIA степень Трансмуральные язвы с очаговым некрозом
IIIB степень Обширный некроз
IV степень Перфорация
1.6 Клиническая картина заболевания или состояния (группы заболеваний или состояний)
Клинические проявления ХОП зависят от характера прижигающей жидкости, концентрации, объема, принятого через рот, что в итоге выражается в степени ожога.
В связи с этим клиническую картину следует рассматривать в зависимости от стадии заболевания (состояния): острой токсикогенной стадии, соматогенной стадии и стадии послеожоговых рубцовых изменений [2,16,23].
а) Острая токсикогенная стадия (первые 3 суток)
При приёме прижигающей жидкости менее 50 мл и кратковременном контакте со слизистой оболочкой полости рта, глотки и пищевода (I степень ожога) пациент ощущает боль при акте глотания, слюнотечение, жажду. Сразу после приёма прижигающий жидкости может быть однократная рвота содержимым желудка. При распространении отёка со стенки глотки на гортань появляется осиплость голоса. Местно на подбородке, в углах губ имеются следы ожогов в виде гиперемии кожи.
Если пациент ограничивает себя в приеме пищи и жидкости и не проводится инфузионная терапия, наблюдается олигурия и задержка стула. В течение недели удерживается субфебрильная температура тела, в анализе крови – умеренный лейкоцитоз. Через 6-8 дней все патологические явления исчезают.
При ожоге II степени сразу после приема прижигающей жидкости возникает резкая боль в полости рта и глотки, которая усиливается при акте глотания, боль в межлопаточной и эпигастральной областях, слюноотделение, многократная рвота с примесью свежей крови.
На подбородке и в углах губ - глубокие ожоги с очагами некроза.
Общее состояние быстро ухудшается. Двигательное возбуждение сменяется адинамией. Кожный покров бледный, выступает холодный пот. Прогрессируют одышка, тахикардия, акроцианоз.
В анализах крови - резкий сдвиг лейкоцитарной формулы влево.
Общее резорбтивное действие при отравлении уксусной кислотой характеризуется коагулопатией, нефро- и гепатопатией.
Токсическая коагулопатия, обусловленная гемолизом, проявляется гиперкоагуляцией, которая затем сменяется гипокоагуляцией. В тяжелых случаях – может развиться ДВС-синдром.
Токсическая нефропатия в зависимости от тяжести отравления или выражается в микрогематурии, снижении клубочковой фильтрации, повышении уровня креатинина, или в развитии острой почечной недостаточности.
Токсическая гепатопатия в зависимости от тяжести отравления выражается или в иктеричности склер с увеличением аспартатаминотрансферазы и лактатдегидрогеназы, или в развитии острой печеночной недостаточности.
При обширных ожогах III-IV степени явления экзотоксического шока нарастают и без лечения пациенты погибают в первые сутки-двое после ожога.
б) Стадия отторжения некротических тканей
У выживших пациентов ожоги на лице к концу первой недели покрываются корочками. Сохраняется болезненная дисфагия и язвенно-некротический эзофагит, который сопровождается кровоточивостью тканей. В таких случаях возникает рвота с примесью крови.
Болезненная дисфагия постепенно уменьшается, вследствие чего некоторые авторы называют эту стадию – стадией мнимого благополучия, но начинается отторжение некротизированных участков пищеводной стенки. Клинически это проявляется многократной рвотой с примесью некротических масс. При одномоментном отторжении большого массива тканей возникает повреждение сосудов пищевода с профузным пищеводным кровотечением.
Этот опасный для жизни период длится две-три недели, после чего острый химический эзофагит стихает, дисфагия уменьшается, и пациент начинает осторожно принимать пищу и жидкость.
Токсикологи выделяют острую соматогенную стадию химических ожогов пищевода (первые 2 недели).
В этой стадии острого отравления возникают ранние (1-2 сутки) или поздние (после 3-х суток) соматогенные осложнения.
К ранним относятся – механическая асфиксия при ожогах рта и верхних дыхательных путей, интоксикационный делирий, острый панкреатит.
К поздним – трахеобронхит, пневмония, поздний интоксикационный психоз.
в) Стадия формирования послеожоговых рубцовых изменений
Клинически формирование рубцовых стриктур в исходе химического ожога пищевода проявляется постепенным развитием нарушения проходимости для пищи и воды. Сначала возникает чувство застревания в пищеводе твердой пищи, затем густой и затем – жидкой, пациент вынужден принимать пищу медленно, маленькими глотками и запивать водой.
При поспешности в еде, заглатывании крупных кусков пищи возникает обтурация просвета пищевода с характерной клинической картиной. У пациента после глотка появляется ощущение давящего комка за грудиной и межлопаточной области. Боль усиливается при акте глотания, появляется слюнотечение.
Необращение за медицинской помощью, самостоятельные попытки устранить обтурацию (приём больших глотков воды, стремление проталкивать пищевую массу через сужения подручными средствами) приводит к разрыву пищевода и смерти от медиастинита.
г) Отдаленные сроки после химического ожога пищевода. Через 15-20 лет в рубцовых тканях нередко развивается плоскоклеточный рак [5].
При достижении опухоли больших размеров, прорастании в соседние органы появляется постоянная глухая боль в межлопаточном пространстве, на которую пациенты с послеожоговыми изменениями пищевода не обращают большого внимания.
2. Диагностика заболевания или состояния (группы заболеваний или состояний) медицинские показания и противопоказания к применению методов диагностики
Критерии установления диагноза
Диагноз химического ожога пищевода устанавливается на основании данных анамнеза (факт перорального приёма химического вещества), жалоб, физикального осмотра (ожог области лица, ротовой полости) и данных инструментального исследования [2,6,11,23].
2.1 Жалобы и анамнез
- При подозрении на химический ожог пищевода рекомендуется обратить внимание на жалобы пациента на боль в полости рта, животе, внезапно возникшую после того, как он выпил из бутылки бесцветную жидкость, приняв её за алкоголь или минеральную воду [2,6,11,16].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 3)
Комментарии: Типичны жалобы на жгучую острую боль в полости рта, в межлопаточной и эпигастральной области, боль при глотании, слюнотечение, осиплость голоса, однократную рвоту с примесью свежей крови [2,6,11,16,42]. Суицидальная попытка имеет свою, известную пациенту мотивацию.
2.2 Физикальное обследование
- У всех пациентов с подозрением на ХОП рекомендуется обратить внимание на наличие следов ожога в области подбородка и уголках губ, оценить слизистую полости рта с целью выявления локальных признаков ожога, а также измерить пульс, артериальное давление с целью определения тяжести состояния [2,6,11,78].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 3)
Комментарии:
а) Острая стадия ожога
При осмотре поведение беспокойное, бледность кожного покрова. При тяжелом отравлении – акроцианоз.
На подбородке и в углах губ - следы ожога в виде гиперемии, отека и очагов некроза кожи.
При осмотре полости рта - отечность и гиперемия слизистых оболочек языка, щек, язычка и дужек, местами - очаги некрозов в виде пленок серого, желтого или черного цвета.
При отравлении уксусной кислотой, формалином или нашатырным спиртом отчётливо ощущается специфический запах. Дыхание самостоятельное. При отравлениях, не сопровождающихся экзотоксическим шоком, одышки нет. Выраженная тахикардия.
При явлениях экзотоксического шока – одышка, бледность, холодный пот, нитевидный пульс, гипотония.
Живот мягкий, болезненный при глубокой пальпации. При сопутствующем ожоге желудка глубокая пальпация недоступна, имеется защитное напряжение мышц, через несколько часов в связи с появлением реактивного выпота в эпигастральной области определяются симптомы раздражения брюшины. В рвотных массах может быть примесь крови.
б) Соматогенная фаза
Клиническая картина обусловлена развитием осложнений. Наиболее демонстративной является клиническая картина пищеводно-желудочного кровотечения.
в) Стадия рубцовых изменений
Данные физикального обследования не специфичны. Пациенты с такой патологией, как правило, пониженного питания.
2.3 Лабораторные диагностические исследования
2.3.1. Клинико-биохимическое обследование
- Пациентам с признаками ХОП рекомендуется выполнить общий анализ крови (клинический анализ крови развернутый), общий (клинический) анализ мочи, биохимический анализ крови общетерапевтический (исследование уровня общего билирубина в крови, исследование уровня билирубина связанного (конъюгированного) в крови, исследование уровня билирубина свободного (неконъюгированного) в крови, определение активности аланинаминотрансферазы в крови, определение активности аспартатаминотрансферазы в крови, исследование уровня мочевины в крови, исследование уровня креатинина в крови, исследование уровня общего белка в крови, исследование уровня глюкозы в крови, исследование уровня натрия в крови, исследование уровня калия в крови, исследование уровня хлоридов в крови, исследование уровня общего кальция в крови), с целью получения информации о состоянии основных жизнеобеспечивающих систем организма и показателей гомеостаза [2,6,11,18, 84-86].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
- Пациентам с признаками ХОП в случае развития нефропатии, гепатопатии, почечно-печеночной недостаточности и другой патологии, в качестве дополнительных методов рекомендуется определение активности альфа-амилазы в моче, определение активности щелочной фосфатазы в крови, определение активности гамма-глютамилтрансферазы в крови, исследование уровня общего белка в крови, исследование уровня альбумина в крови с целью оценки функции почек [2, 18].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
Комментарии: Кратность проведения этих исследований зависит от тяжести отравления и длительности пребывания пациента в стационаре. Определение по степени тяжести отравления на основании лабораторных данных представлено в Приложении А3.
2.3.2. Химико-токсикологическая лабораторная диагностика
- У пациентов с отравлением уксусной кислотой с целью оценки тяжести поражения рекомендуется определение наличия и уровня свободного гемоглобина в крови и моче [3,6, 87].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств 4)
Комментарии: Определить в биосредах организма кислоту или щелочь не представляется возможным.
Содержание свободного гемоглобина в крови при легкой степени гемолизе составляет 5 г/л, при средней тяжести – 5-10 г/л, при тяжелой степени – свыше 10 г/л.
Свободный гемоглобин в моче появляется при содержании его в плазме свыше 1-1,5 г/л и проявляется изменением окраски мочи от красного до вишневого, в зависимости от уровня гемоглобинурии. Следует при этом иметь в виду, что отсутствие гемолиза при наличии других признаков не исключает отравления уксусной кислотой.
2.4 Инструментальные диагностические исследования
- У пациентов с ХОП в острой фазе при наличии болевого синдрома перед выполнением инструментальных исследований рекомендуется премедикация анальгетиками и спазмолитическими препаратами (папаверин и его производные,) в стандартной дозировке [2, 11, 73, 74].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций C (уровень достоверности доказательств 5)
2.4.1. Рентгенологическое исследование
- Пациентам с клиническими признаками ХОП рекомендуется выполнение обзорной рентгенографии органов грудной клетки (прицельная рентгенография органов грудной клетки/рентгенография лёгких цифровая) с целью выявления воздуха в средостении, что предполагает перфорацию пищевода, а также свободный воздух под диафрагмой, указывающий на перфорацию желудка [11,71].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств 3)
- Пациентам с клиническими признаками ХОП рекомендуется выполнение рентгеноконтрастного исследования пищевода (рентгенография пищевода с контрастированием, рентгенография пищевода с двойным контрастированием) с целью определения распространённости и глубины поражения пищевода и желудка [2, 72].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций C (уровень достоверности доказательств 5)
Комментарии: Рентгеноконтрастное исследование пищевода является неинвазивным и высокоинформативным методом диагностики. Если необходимо подтвердить клинически подозреваемую перфорацию, можно использовать водорастворимые рентгеноконтрастные средства, содержащие йод, обладающие менее раздражающим действием, чем бария сульфат ** [72]. И наоборот, бария сульфат ** должен быть предпочтительным контрастным средством при позднем исследовании, обеспечивая большую рентгенографическую детализацию, чем водорастворимые рентгеноконтрастные средства, содержащие йод [48,71].
Методика рентгенологического исследования в стадии ожогового эзофагита (гастрита) и отторжения некротизированных тканей.
После обзорной рентгенографии органов грудной клетки и брюшной полости пациенту дают глоток водорастворимого рентгеноконтрастного средства, содержащего йод, прослеживая функцию надгортанника и акт глотания. При отсутствии аспирации исследование продолжают с взвесью бария сульфата**, которая хорошо контурирует рельеф стенок пищевода и желудка.
Рентгенологические признаки ожога пищевода
I степень ожога. Глотание не затруднено, просвет пищевода обычный, складки слизистой оболочки хорошо прослеживаются, но местами утолщены до 5 мм. Перистальтика сохранена, единичные признаки регургитации.
II степень ожога. Глотание болезненное, мелкими порциями. Просвет пищевода сужен, складки слизистой оболочки сглажены, местами не определяются. Стенка пищевода неэластична, не перистальтирует. Отмечается спазм на различных уровнях и частая регургитация.
III-IV степени ожога. Глотание резко болезненное, затруднённое. Просвет пищевода расширен до 4-6 см в поперечнике, содержит жидкость. Стенки пищевода атоничны, не перистальтируют. Рельеф слизистой оболочки не определяется, в местах отторжения тканей - плоские ниши.
Рентгенологические признаки ожога желудка
I степень ожога. Желудок гипотоничен, содержит жидкость и слизь. Контуры ровные, перистальтика отчётливая. Складки слизистой оболочки утолщены. Отмечается кратковременный спазм привратника.
II степень ожога. Желудок гипотоничен, содержит много жидкости и слизи. Контуры ровные, но перистальтика вялая. Складки слизистой оболочки утолщены и сглажены. Множественные стойкие депо бария сульфата**. Эвакуация замедлена.
III-IV степени ожога. Желудок атоничен, переполнен содержимым. Перистальтики нет. Складки слизистой оболочки резко утолщены или не прослеживаются. Множественные депо бария сульфата** – плоские (эрозии) и глубокие (язвы). Длительный спазм привратника.
Методика рентгенологического исследования в стадии развития грануляционной ткани, формирования рубцов и стойких послеожоговых изменений
- Пациентам с химическим ожогом пищевода в стадии развития грануляционной ткани, формирования рубцов и стойких послеожоговых изменений рекомендуется выполнение рентгенографии пищевода, дополненное обязательной рентгенографией желудка и двенадцатиперстной кишки с целью локализации стриктур, их протяжённости, обнаружения признаков поражения желудка и двенадцатиперстной кишки [2, 4].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций C (уровень достоверности доказательств 5)
Комментарии: Вид и консистенция контрастного средства используются в зависимости от степени сужения пищевода. При непроходимости пищевода для жидкой взвеси бария сульфата** или клинической картине пищеводно-трахеального (пищеводно-бронхиального) свища, используют водорастворимые рентгеноконтрастные средства, содержащие йод. Исследование проводят в вертикальном и горизонтальном положении пациента.
При контрастировании пищевода необходимо установить наличие стриктуры, ее локализацию и протяжённость (верхняя и нижняя границы по отношению к телам позвонков), минимальный и максимальный диаметр сужения и супрастенотического расширения, расположение входа в стриктуру (по центру, эксцентрически). У пациентов со множественными стриктурами указывают их локализацию, протяжение, диаметр пищевода между сужениями. Рубцовые изменения выглядят как сужения просвета пищевода с неровными, зазубренными краями.
Желудок может быть нормальных размеров, уменьшен или увеличен, что зависит от локализации и распространенности рубцовых изменений. При стенозе в области тела, субтотальном и тотальном сужении желудок выглядит как «сморщенный». При изолированном стенозе выходного отдела наблюдается расширение его просвета. При резком стенозе рубцовые ткани выглядят как узкая трубка с неровными краями, что напоминает рентгенологическую картину рака желудка. При полной обтурации выходного отдела супрастенотическая часть выглядит как мешок с конусом, обращенным к привратнику. У пациентов с полной непроходимостью пищевода исследование проводят через гастростому.
- Пациентам с ХОП и клиническими признаками экзотоксического шока, а также нарушением глотания и проходимости пищевода, рентгеноконтрастное исследование не рекомендуется из-за угрозы аспирации [2].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций C (уровень достоверности доказательств 5)
2.4.2. Эндоскопический метод исследования
Эндоскопия в стадии ожогового эзофагита (гастрита) и отторжения некротических тканей
- Пациентам с клиническими признаками ХОП рекомендуется выполнение эзофагогастродуоденоскопии (ЭГДС) в первые 12 – 48 часов после травмы с целью оценки распространённости и глубины поражения [9,11,16,23,41].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций В (уровень достоверности доказательств 3)
Комментарии: ЭГДС считается решающим методом в диагностике ХОП и обычно рекомендуется в первые 12-48 ч после попадания в ЖКТ химического вещества прижигающего действия, хотя эндоскопия безопасна и надежна до 96 ч после травмы [40,75,76]. По некоторым данным ЭГДС выполнялись без последствий и в более поздние сроки - от 5 до 15 дней после химического ожога [43], тем не менее, эндоскопия в этот период потенциально опасна перфорацией стенки пищевода из-за истонченности его тканей.
В тоже время, недостаточная точность эндоскопического метода в определении глубины химического повреждения может стать причиной ошибочной лечебной тактики с непредсказуемыми последствиями [4,7,10,11,17, 22,23,46].
- Пациентам с клиническими признаками ХОП с целью диагностики в течение первых 12 часов после непосредственного воздействия ВПД рекомендуется ЭГДС при невозможности проведения КТ [4, 6, 11, 23].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств 5)
Комментарии: Согласно ряда исследований необходимость в экстренной эндоскопической оценки степени ожога пищевода и желудка сводится к ситуациям, когда КТ не может быть использована (отсутствует в медицинской организации, противопоказано внутривенное контрастирование, у пациентов детского возраста и когда при КТ предполагается трансмуральный некроз пищевода, но интерпретация данных затруднена/сомнительна) [11,23].
- Пациентам с клиническими признаками ХОП выполнение диагностической эзофагогастродуоденоскопии спустя 4 дня после травмы не рекомендуется из-за риска перфорации пищевода [9,11,23,41,43].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств 5)
Комментарий: В период от 5 дней до 3 недель после травмы стенка пищевода наиболее уязвима, риск перфорации при эндоскопии весьма высок. Следовательно, в эти сроки проведение эндоскопического исследования крайне нежелательно, а показания к нему должны быть сведены к минимуму: выраженная дисфагия, желудочно-кишечное кровотечение [11,43,46].
- Пациентам с клиническими признаками ХОП проведение эндоскопии (ЭГДС) с диагностической целью не рекомендуется при нестабильной гемодинамике, при рентгенологических признаках перфорации пищевода и медиастинита, ожоге надгортанника с его отеком, ожоге гортани и глотки третьей степени, которые могут быть предвестником закупорки дыхательных путей, а также при ожоге дыхательных путей, что требует эндотрахеальной интубации или трахеостомии [11,22,40,44, 45,46].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств 5)
Комментарий: Ожог надгортанника с его отеком, ожог гортани и глотки третьей степени могут быть предвестником закупорки дыхательных путей, как и ожог дыхательных путей, указывают на необходимость эндотрахеальной интубации или трахеостомии [11,22].
При отсутствии противопоказаний исследование проводят натощак с премедикацией 1 мл 0,1% раствора атропина** и под местной анестезией опрыскиванием лидокаином**. Адекватная седация (общая анестезия у детей) является обязательной. Эндотрахеальная интубация необходима только для пациентов с нарушением дыхания. Важным моментом является крайняя осторожность и минимальная инсуффляция воздуха [2,11,22,23].
При дисфагии применяют фиброэндоскопы малого диаметра (PF-28, PF-24).
Положение пациента на левом боку с опущенным головным концом стола для предупреждения аспирации слюны или желудочного содержимого.
Выполняют осмотр ларингоскопом полости рта и гортаноглотки. После проведения эндоскопа в просвет пищевода отмечают состояние слизистой оболочки, локализацию наложений фибрина и очагов некроза, наличие желудочно-пищеводного рефлюкса и состояние кардиального жома.
При осмотре желудка фиксируют степень ожога и преимущественную его локализацию, выражая площадь ожога в квадратных сантиметрах и отмечая анатомические отделы: привратник, антральный отдел, тело, малая и большая кривизна, передняя и задняя стенка, область кардии. Чаще всего изменения находят в антральном отделе и на задней стенке.
- Для определения степени ожога пищевода и желудка рекомендуется использовать эндоскопическую классификацию, предложенную Волковым С.В. (1997) и дополненную Песней-Просоловой Е.А. (2006) [7].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств 4)
Комментарий: В первые сутки после ожога I-II степени на слизистой оболочке отмечается наличие коагуляционных пленок белесого цвета, которые повторяют рельеф (складки) слизистой оболочки и не снимаются механическим путём. Очаги некроза имеют темно-коричневый или черный цвет. В нижних отделах пищевода некротические ткани окрашиваются в тёмно-жёлтый или тёмно-зелёный цвет при наличии заброса желчи.
При отторжении струпа (3-4 сутки) видна темно-красная грануляционная ткань. После состоявшегося пищеводного кровотечения на поверхности грануляций видны мелкие тромбы в просвете сосудов подслизистого слоя.
Позже этих сроков обнаруженная неравномерность роста грануляции с избыточным образованием в краях послеожоговых язв, служит признаком формирования рубцовых деформаций и стриктур.
Данные, полученные при эндоскопическом исследовании, во многом прогнозируют тяжесть и длительность течения острой стадии ожога пищевода и желудка.
Эндоскопия в стадии развития грануляционной ткани, формирования рубцов и стойких послеожоговых изменений
- Всем пациентам с ХОП в стадии развития грануляционной ткани, формирования рубцов и стойких послеожоговых изменений с целью оценки локализации, протяженности стеноза и определения показаний к необходимости лечебных манипуляций (бужирования, дилатация, стентирования) рекомендуется выполнение ЭГДС через 3 недели после травмы [7-10,11,40].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств 5)
Комментарий: Через три недели после ХОП, как правило, формируются плотные фиброзные ткани, и выполнение эндоскопического исследования становится более безопасным (возможно выполнение исследования под местной анестезией) [10,11,40].
Эндоскопическая классификация рубцовых стенозов пищевода (Ю.И. Галлингер и соавт. 2000) предполагает четыре степени сужения [38]:
I степень - диаметр пищевода в зоне сужения составляет 9-11 мм (через стриктуру проходит среднекалиберный гастроинтестинальный эндоскоп);
II степень - просвет пищевода в зоне сужения составляет 6-8 мм (проходит бронхофиброскоп диаметром 5,5-7 мм);
III степень - диаметр пищевода в зоне сужения составляет 3-5 мм (проходит ультратонкий эндоскоп диаметром 2,4-2,8 мм, а если он не применяется, то просвет сужения оценивается по диаметру струны или катетера);
IV степень - просвет сужения составляет 1-2 мм или вовсе отсутствует (ниже зоны сужения удается провести только направляющую струну, за исключением случаев полной облитерации).
У пациентов с рубцовым стенозом желудка эндоскопия позволяет уточнить диаметр стриктуры, выяснить выраженность и распространенность морфологических изменений в супрастенотическом отделе желудка для определения объема резекции органа или места формирования обходного анастомоза, возможности выполнения кокой-либо дренирующей желудок операции.
- У пациентов с дисфагией для оценки изменений в ротоглотке, глоточно-пищеводном переходе, супрастенотическом отделе пищевода эндоскопическое исследование рекомендуется начинать с использования среднекалиберных гастроинтестинальных эндоскопов [7].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств 5)
Комментарий: Первичное использование эндоскопов малого диаметра может привести к тому, что нерезко выраженные рубцовые изменения, чаще всего небольшие по протяженности, которые локализуются в области входа в пищевод, будут пропущены.
Эндоскоп следует вводить только под визуальным контролем. Складки в области глоточных синусов и глоточно-пищеводного перехода раздвигают дистальным концом эндоскопа, понемногу инсуффлируя воздух. В тех случаях, когда выраженные рубцовые изменения в глотке и в области входа в пищевод отсутствуют и эндоскоп удается провести в шейный отдел пищевода, следует оценить состояние слизистой оболочки и диаметр супрастенотического отдела пищевода вплоть до зоны наибольшего сужения; по расстоянию от резцов установить верхнюю границу рубцового процесса и оценить диаметр сужения, сравнивая его с эндоскопом, который удается провести через все сужение или его часть, либо с инструментом, размер которого известен – струна, катетер, биопсийные щипцы. Просвет пищевода в зоне стеноза является объективным критерием, от которого в основном зависит выраженность дисфагии. Если удается преодолеть область сужения гастроинтестинальным эндоскопом среднего калибра, то оценивают состояние слизистой оболочки и протяженность стриктуры, осматривают нижележащие отделы пищевода, а затем желудок и двенадцатиперстную кишку. Участки рубцовых изменений стенки пищевода могут чередоваться с непораженными, в этих случаях необходимо говорить о стриктурах двойной или множественной локализации. При малейшем подозрении на возможность злокачественного процесса следует брать материал для гистологического и цитологического исследований.
При невозможности провести гастроинтестинальный эндоскоп через сужение для дальнейшего осмотра необходимо применение малокалиберных эндоскопов (гастроскопов малого диаметра – от 4,8 до 5,9 мм, уретерескопов диаметром 3,5-3,7 мм, холедохоскопов, в частности, Spyglass, диаметром 3 мм) для оценки протяженности стеноза, его выраженности на различных уровнях, локализации, количества сужений, диагностики возможных осложнений (свищи, малигнизация), состояния слизистой оболочки как в зоне стеноза, так и в нижележащих отделах пищевода, желудка, двенадцатиперстной кишки. Приборы, которые не предназначены для осмотра желудочно-кишечного тракта, не оснащены помпой для подачи воздуха и воды, поэтому воздух нужно подавать вручную порционно с помощью резиновой «груши», которая прикрепляется к порту биопсийного канала. Если эндоскоп удалось провести ниже зоны сужения, то это позволяет безопасно, надежно, провести направляющую струну с целью последующего эндоскопического лечения. Однако даже в тех случаях, когда не удается преодолеть весь стенозированный участок, то использование эндоскопов малого диаметра после среднекалиберных позволяет в целом ряде случаев при двойных и множественных сужениях вплотную подойти к верхнему краю основной зоны стеноза и провести направляющую струну под визуальным контролем верхнего края, особенно если вход во второе сужение расположен эксцентрично или имеются дивертикулоподобные карманы между двумя сужениями.
При невозможности проведения ни одного из эндоскопов через зону сужения и при наличии гастростомы для полноценного осмотра постстенотического отдела пищевода целесообразно выполнять ретроградную гастроэзофагоскопию. В положении пациента на левом боку после удаления гастростомической трубки эндоскоп через стому вводят в желудок, проводят вверх по малой кривизне по направлению к кардии. Затем дистальный конец эндоскопа прижимают к кардии и при небольшой инсуффляции воздуха прибор проводят в пищевод вплоть до нижнего края стеноза. После этого следует осмотреть желудок и двенадцатиперстную кишку, которая доступна осмотру в большинстве случаев. Достаточно важным является определение положения наложенной гастростомы: в тех случаях, когда отсутствует грубая рубцовая деформация желудка и гастростома наложена близко к малой кривизне, большая кривизна может быть использована для выкраивания трансплантата при решении вопроса в пользу эзофагопластики [7].
2.4.3. Компьютерная томография
- Пациентам 18 лет и старше с клиническими признаками ХОП рекомендуется выполнение экстренной КТ органов грудной полости (компьютерная томография органов грудной полости с внутривенным болюсным контрастированием, мультипланарной и трехмерной реконструкцией, компьютерная томография пищевода с пероральным контрастированием) с целью уточнения локализации, объёма и глубины поражения при условии адекватной функции почек [9-12, 20,22,25].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций B (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2)
Комментарии: Экстренная КТ пищевода имеет ряд преимуществ перед эндоскопией при ранней диагностике химических повреждений пищевода и желудка. К ним относятся: неинвазивность, возможность оценки кровоснабжения всех слоев пищевода и желудка, состояние окружающей клетчатки и тканей [9-12,20]. КТ предполагает более подробную оценку трансмурального повреждения стенок пищевода и желудка и степени некроза, чем ранняя эндоскопия [22,77], более ценно, чем эндоскопия, при оценке угрозы или установленной перфорации желудка [13].
Применение метода ограничено у пациентов с острой почечной недостаточностью ввиду низкой информативности нативного исследования и противопоказаний к выполнению внутривенного контрастного усиления.
Предложена система оценки КТ для прогнозирования стриктуры пищевода [11].
Чувствительность и специфичность КТ в определении тяжести химических повреждений пищевода умеренно выше по сравнению с эндоскопией, что позволяет точнее прогнозировать послеожоговые осложнения.
Данные КТ-исследования при ожоговой травме пищевода позволяют прогнозировать как ранние, так и поздние осложнения и выработать тактику лечения [11,13,28].
При ожоге I степени развитие осложнений маловероятно. При II степени имеется вероятность развития стриктур пищевода, что требует применения профилактических мер. При поражении III степени – развитие стриктуры неизбежно. Изменения IV степени свидетельствуют о трансмуральном поражении пищевода с крайне высоким риском развития некроза и перфорации, что требует выполнения неотложной эзофагэктомии.
КТ – более эффективный инструмент для ранней диагностики необратимых изменений пищевода и желудка после химической травмы, чем стратегия, основанная на эндоскопической картине и клинико-лабораторных признаках [18].
Решение о необходимости срочной эзофагэктомии при химических повреждениях пищевода должно быть основано на результатах КТ, свидетельствующих о трансмуральном некрозе (нечеткость стенки пищевода и параэзофагеальной клетчатки, отсутствие накопления контрастного средства в стенке пищевода при контрастном усилении). Подобный подход позволяет избежать необоснованных эзофагэктомий и эксплоративных лапаротомий [20,21].
Таким образом, КТ должна рассматриваться как более чувствительный метод в диагностике повреждений пищевода и желудка при химических ожогах. В то же время, корреляция между эндоскопией и КТ относительно градации повреждений недостаточно высока, чтобы полностью исключить необходимость в эндоскопическом исследовании, особенно в первые 12-48 часов после приема ВПД [9,22].
В стадии развития грануляционной ткани, формирования рубцов и стойких послеожоговых изменений КТ позволяет определить выраженность воспалительных и рубцовых послеожоговых изменений пищеводной стенки и параэзофагеальной клетчатки [23].
- Нет данных по эффективности КТ в диагностике ХОП у детей, поэтому систематическое использование КТ не может быть рекомендовано в этой группе из-за редкости тяжелых травм и пожизненных рисков радиационного облучения [22,23].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
Комментарий: КТ может быть полезна у детей с клиническими, эндоскопическими признаками обширного поражения пищевода, которым предстоит хирургическое вмешательство.
2.5 Иные диагностические исследования
- Пациентам с ХОП при высоком риске перфорации желудка по данным эндоскопии рекомендуется диагностическая лапароскопия с целью исключения перитонита [34,78].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 4)
Комментарий. Лапароскопия является полезным дополнением при оценке пациента с высоким риском перфорации желудка, наблюдаемого при эндоскопии, или пациентов с тяжелым поражением пищевода, у которых эндоскопия верхних отделов желудочно-кишечного тракта для оценки состояния желудка невозможна [34,78].
3. Лечение, включая медикаментозную и немедикаментозную терапии, диетотерапию, обезболивание, медицинские показания и противопоказания к применению методов лечения
3.1. Лечение в острой стадии отравления ВПД
3.1.1. Консервативное лечение
- Пациентам с ХОП в острой стадии отравления ВПД рекомендуется немедленная комплексная терапия, включающая быстрое удаление токсиканта из желудочно-кишечного тракта, местное лечение и детоксикацию с коррекцией нарушений органов и систем, развивающихся при ожоговой болезни [3,4,6,11,12,13,19,24,45].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций C (уровень достоверности доказательств – 3)
Комментарий: Промывание желудка через зонд наиболее эффективно, безопасно и не имеет противопоказаний в первые 6 ч после приема ВПД, в дальнейшем эффективность значительно снижается в связи с завершением резорбции этого вещества, а по прошествии 12 ч промывание желудка неэффективно [3,19,24].
- Пациентам с ХОП промывание желудка без использования зонда и с искусственным вызыванием рвоты с целью удаления токсиканта не рекомендуется [4,11,19].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 3)
Комментарий: Промывание желудка без использования зонда с искусственным вызыванием рвоты является крайне опасным, поскольку повторное прохождение токсиканта по пищеводу усиливает степень его ожога. Кроме того, при этом существует опасность аспирации прижигающей жидкости и развития ожога дыхательных путей [4,11,19].
- Пациентам с ХОП введение в ЖКТ раствора натрия гидрокарбоната** с целью нейтрализации кислот не рекомендуется [4,11,23].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 3)
Комментарий: Применение раствора натрия гидрокарбоната** с целью нейтрализации кислот недопустимо, так как вызывает острое расширение желудка образующимся углекислым газом и усиление кровотечения. В качестве нейтрализующего средства может служить окись магния (жженая магнезия) в виде водной взвеси 10-20 г. порошка в 2 л. воды или Алгелдрат+Магния гидроксид внутрь с последующим промыванием желудка [4,24].
- Пациентам с признаками ХОП рекомендуется назначение анальгетиков (опиоиды, другие анальгетики-антипиретики), атропина**, папаверин и его производные с целью купирования болевого синдрома, уменьшения тонуса ЖКТ [1-4,7,8,24]
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций B (уровень достоверности доказательств – 3)
Комментарий: Лечение болевого синдрома включает введение опиоидов (морфин**, тримеперидин**, Кодеин+Морфин+Носкапин+Папаверин+Тебаин) или нестероидных противовоспалительных и противоревматических препаратов (кеторолак**) , других анальгетиков и антипиретиков метамизол натрия по 1 мл 3-4 раза в сутки), алкалоидов белладонны, третичных аминов (A03BA) (1 мл 0,1% раствора атропина** 2 раза в сутки), папаверина и его производных (2 мл 2 % раствора папаверина или 2 мл дротаверина** внутримышечно, или 1 мл 0,2 % раствора платифиллина**) подкожно до 4 раз в сутки, глюкозоновокаиновой смеси (500 мл 5 % раствора дектрозы** и 50 мл 2 % раствора прокаина**) 2-3 раза в сутки в/в.
- При компенсированном стенозе гортани пациентам с ХОП рекомендуется внутривенное введение и ингаляция кортикостероидов системного действия совместно с холинолитиками (АТХ алкалоиды белладонны, третичные амины), адренергическими средствами для ингаляционного введения (АТХ адренергические и дофаминэргические средства) с целью устранения отёка и восстановления бронхиальной проходимости [1-4,7,8,11, 13, 15,19,23].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 3)
- Пациентам с ХОП в случае нарастания стеноза гортани и угрозы асфиксии рекомендуется трахеостомия (или коникотомия) с целью активной аспирации секрета из трахеи и крупных бронхов и санации дыхательных путей [1-4,7,8,11, 13, 15,19,23].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 3)
Комментарий: Трахеостомия при отравлении ВПД имеет определенные преимущества перед интубацией трахеи для восстановления проходимости верхних дыхательных путей, поскольку позволяет пациенту находиться в сознании, активно откашливать мокроту [1-4,7,8, 15,19,23].
- Пациентам с признаками отравления ВПД и экзотоксического шока рекомендуется внутривенное введение кровезаменителей и препаратов плазмы крови, гипертонического раствора декстрозы** с инсулинами короткого действия и их аналогами (для повышения действия декстрозы), с целью повышения коллоидного осмотического внутрисосудистого давления и препятствия выходу внутрисосудистой жидкости [1-4,7,8,15,19].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
Комментарий: В целом, лечение пациентов с признаками экзотоксического шока соответствует общим принципам реанимационного ведения пациентов в состоянии шока. Объем инфузионной терапии определяется тяжестью расстройств гемодинамики и уровнем восстановления гемодинамических параметров, гематокрита, ЦВД. Пациентам с декомпенсированным шоком проводят быстрое струйное введение коллоидных растворов (АТХ Кровезаменители и препараты плазмы крови). Интенсивное введение жидкости продолжается до повышения гемодинамических показателей на 45-50 % по сравнению с исходным уровнем, затем переходят на капельное вливание растворов, вводят от 3 до 15 литров жидкости в сутки.
Особое внимание уделяют устранению метаболических нарушений. Для коррекции ацидоза применяют ощелачивание плазмы, внутривенное введение 4% раствора натрия гидрокарбоната** [1-4,7,8,15,19].
Пациентам с ХОП с целью лечения ранних вторичных кровотечений рекомендуется проведение мероприятий по усилению гемостаза в месте кровотечения, а также угнетению внутрисосудистой коагуляции с целью профилактики микротромбообразования, при этом введение гепарина натрия** рекомендуется только при условии локальной остановки кровотечения [1-4,7,8].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
Комментарий: Раннее первичное кровотечение вследствие компенсаторной гиперкоагуляции быстро прекращается. Лечение ранних вторичных кровотечений ведется по двум направлениям: усиление гемостаза в месте кровотечения и одновременное угнетение общей внутрисосудистой коагуляции с использованием группы гепарина. Наилучшим местным гемостатическим эффектом обладает локальная гипотермия пищевода и желудка с использованием специальных аппаратов и зондов. Она уменьшает кровоток по сосудам желудка (на 67%), способствует агрегации форменных элементов, локально уменьшает фибринолитическую активность, что создает благоприятные условия для местного тромбообразования.
Введение препаратов группы гепарина с целью профилактики микротромбообразования показано только при условии локальной остановки кровотечения. Локальная гипотермия желудка неэффективна при развитии у пациента афибриногенемии. В этих случаях для остановки кровотечения можно прибегнуть к замораживанию слизистой оболочки желудка.
- При поздних кровотечениях у пациентов с отравлением ВПД гепаринотерапия не рекомендована, рекомендуется проведение стандартной гемостатической терапии [1-4,7,8].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
Комментарий: При поздних кровотечениях гепаринотерапия противопоказана, а локальная гипотермия желудка менее эффективна. Проводится стандартная гемостатическая терапия: голод, дробное переливание эритроцитов, плазмы крови, фибриногена.
- С целью профилактики поздних кровотечений у пациентов с отравлением ВПД рекомендуется использовать препараты-ингибиторы протонного насоса и антациды [1-4,7,8, 11].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 3)
- При возникновении поздних кровотечений у пациентов с отравлением ВПД рекомендуется использовать методы эндоскопического гемостаза (Остановка кровотечения из периферического сосуда эндоскопическая с использованием электрокоагуляции (термокоагуляции) [1-4,7,8].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
Комментарий: Так как источниками кровотечения являются мелкие сосуды подслизистого слоя, кровотечение останавливают эндоскопической лазерной коагуляцией, которая не вызывает значительного дополнительного повреждения стенки пищевода [1-4,7,8].
- Пациентам с признаками отравления ВПД с целью лечения токсической коагулопатии и профилактики микротромбообразования рекомендуется применение антитромботических средств (антикоагулянтов) [1-4,7,8,92].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций B (уровень достоверности доказательств – 3)
Комментарий: Антитромботические средства (антикоагулянты) рекомендуется использовать еще до развития выраженного синдрома токсической коагулопатии (табл. 1). При токсической коагулопатии I стадии (гиперкоагуляция) лечение антитромботическими средствами осуществляют, контролируя время свертывания перед каждой инъекцией.
Во II (гипокоагуляция) и в III (фибринолиз) стадиях лечение осуществляют, контролируя содержание фибриногена и число тромбоцитов каждые 4 ч до момента, когда эти показатели начнут повышаться. В дальнейшем ежедневно в период всего лечения антитромботическими средствами (например, лекарственными препаратами группы гепаринами) осуществляется контроль с помощью развернутой коагулограммы (ориентировочного исследования системы гемостаза) [92] .
Таблица 1
Схема антикоагулянтной терапии токсической коагулопатии при отравлении уксусной эссенцией
|
Степень тяжести отравления |
Доза гепарина натрия ** [92], ЕД/сут |
Способ введения и длительность лечения |
|
Легкая |
5000 |
Подкожно 1-2 сут |
|
Средняя |
5000 - 10000 |
Подкожно 4-5 сут |
|
Тяжелая при содержании свободного Нb в плазме менее 10 г/л |
10 000 - 40 000 |
Подкожно 4-6 сут |
|
Тяжелая с концентрацией свободного Нb в плазме свыше 10 г/л |
20 000 - 80 000 30 000 - 40 000 |
Внутривенно 4-6 сут |
- С целью профилактики инфекционных осложнений у пациентов с отравлением ВПД рекомендуется назначение антибиотиков (бета-лактамные антибактериальные препараты: пенициллины) [2,3].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
- С целью профилактики рубцового сужения пищевода или желудка у пациентов с отравлением ВПД рекомендуется введение глюкокортикоидов, доза конкретного лекарственного препарата подбирается индивидуально в соответствии с инструкцией и в зависимости от тяжести отравления. [1,88-90].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций B (уровень достоверности доказательств – 3)
Комментарий: Длительность лечения определяется тяжестью ожога: при легком ожоге – 7 суток, средней тяжести - до 20 суток, при тяжелом - не менее 30 суток. Указанный курс лечения должен быть проведен в условиях стационара, в дальнейшем лечение может быть продолжено в амбулаторных условиях: при легком ожоге – 3 нед., при ожоге средней тяжести – 1 мес., при тяжелом ожоге – до 2 мес. [1-4,7,8].
- Пациентам с признаками отравления ВПД рекомендуется ранняя адекватная нутритивная поддержка с целью коррекции расстройства белкового и энергетического обмена [1-4,7,8].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
Комментарий: Ранняя адекватная нутритивная поддержка является наиболее эффективным методом коррекции расстройства белкового и энергетического обмена при критических состояниях, обязательной составляющей комплекса интенсивной терапии. Она позволяет добиться сокращения частоты вторичных кровотечений, нозокомиальных пневмоний, уменьшить длительность пребывания пациентов в палате реанимации и интенсивной терапии и сроки пребывания пациента в стационаре.
Пероральное питание является своеобразным «бужирующим» пищевод мероприятием. Объем пищи на один прием составляет 100-150 мл до 5-6 раз в сутки. Пища должна быть щадящей механически и химически. Нежелательные последствия могут возникнуть как при слишком раннем расширении рациона питания, так и при слишком длительном его ограничении. При кровотечении назначается голод.
При легкой степени ожога пищевода и желудка в 1-ю неделю назначают жидкую щадящую диету (№1б). При ожоге желудка средней тяжести назначают диету (№1б) до 2 недель с последующим переводом на стол № l.
При тяжелой степени ожога в первые дни глотание обычно нарушено, в связи с чем, проводится парентеральное или энтеральное зондовое питание. Как только глотание восстанавливается, на протяжении 5-7 суток назначают индивидуальную диету: молоко, кисель, желе, бульоны, затем переводят на диету № 1. Впоследствии назначается диета № 1 на длительный срок в зависимости от течения хронического гастрита. Так как щадящие диеты не могут обеспечить повышенную потребность в белках, во всех случаях рацион восполняется полноценными белками (яйца всмятку, творог, блюда из отварного мяса), а также витаминами. По мере уменьшения болей при глотании пациентов переводят на диету № 1 на длительный срок в зависимости от течения хронического гастрита.
Ранняя диагностика синдрома белково-энергетической недостаточности должна проводится на основании лабораторных маркеров нутритивного статуса: общего белка, альбумина, трансферрина, абсолютного количества лимфоцитов в периферической крови.
Энтеральную нутритивную поддержку проводят следующими методами:
- при сохраненной функции глотания, питательная смесь дается через рот в виде напитка (пероральный метод);
- при наличии у пациента дисфагии питательная смесь вводится через зонд в желудок (назогастральный метод);
- при тяжелых химических ожогах желудка питательная смесь вводится через кишечный зонд, который устанавливается за связку Трейца при проведении ФЭГДС (назоинтестинальный метод).
Выбор метода проведения энтеральной нутритивной поддержки проводят исходят из тяжести состояния пациента при проведении ФЭГДС.
- Энтеральное питание рекомендуется начинать с первых суток после поступления пациента по нарастающей схеме, достигая калоража 2500 ккал/ сутки и белковой квоты 100 г/сутки [1-4,7,8].
- Пациентам с признаками отравления ВПД рекомендуется назначение ингибиторов протонного насоса с целью купирования явлений рефлюкс–эзофагита [1-4,7,8].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
Комментарий: Так как химический ожог пищевода сопровождается, как правило, рефлюкс-эзофагитом, для купирования гиперацидности следует применять ингибиторы протонового насоса. В остром периоде, когда затруднено глотание, препарат назначают парентерально. Для введения в виде внутривенной инфузии содержимое флакона (20 мг рабепразола) сначала растворяют в 5 мл воды для инъекций**, а затем добавляют к инфузионному раствору (0,9% раствор натрияхлорида**) объемом 100 мл и вводят на протяжении 15-30 минут [1-4,7,8].
3.1.2. Хирургическое лечение
- Пациентам с клинико-инструментальными признаками или крайне высоким риском перфорации пищевода и/или желудка на фоне химического ожога рекомендуется экстренное хирургическое лечение [4,8,11,23,32].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций C (уровень достоверности доказательств – 3)
Комментарий: Перфорация пищевода и желудка при этом может быть как в результате трансмурального некроза, так и инструментальной этиологии (ЭГДС, зондирование желудка). Тактика хирургического лечения в подобных ситуациях должна быть основана (при технической возможности) на данных КТ с внутривенным контрастированием, свидетельствующих о необратимых изменениях стенки пищевода и желудка. Подобный подход позволяет избежать необоснованных эзофагэктомий и эксплоративных лапаротомий [20,23].
Эзофагогастрэктомия, выполняемая с использованием комбинированного абдоминального и шейного доступа, является наиболее распространенной экстренной операцией, выполняемой для лечения тяжелых ожогов ВПД, при этом летальность достигает 25 – 34% [23]. Если некроз ограничен желудком, следует рассмотреть возможность гастрэктомии с сохранением пищевода. Резекции желудка целесообразно избегать, поскольку продолжающийся некроз может отрицательно повлиять на исход. Обоснованность эзофагэктомии с сохранением желудка на основании изолированного некроза пищевода подвергается сомнению. Сопутствующий некроз других органов брюшной полости (двенадцатиперстная кишка, поджелудочная железа, селезенка, тонкая и толстая кишка) оправдывает расширенные резекции у 20% пациентов, перенесших эзофагогастрэктомию. Панкреатодуоденумэктомия или удаление двенадцатиперстной кишки может быть выполнено у небольшого числа (6%) пациентов с дуоденальным некрозом (вовлечение поджелудочной железы встречается редко). Панкреатодуоденумэктомия по поводу химических повреждений сопровождается высокой летальностью (39–50%). Наличие обширного некроза кишечника требует обсуждения отказа от операции в каждом конкретном случае из-за низкой выживаемости [23].
3.2. Лечение в стадии формирования рубцовых стриктур
- Пациентам с формирующимися после химического ожога рубцовыми стриктурами рекомендуется бужирование пищевода, как основной метод лечения [11, 23,38,47,49,54,59,62].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций C (уровень достоверности доказательств – 3)
- Применение в ранней стадии формирования рубцовой ткани ее рассечение игольчатым электродом под контролем эзофагоскопии не рекомендуется [38,49].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
Комментарий: Рассечение формирующейся рубцовой ткани под контролем эндоскопа чревато повреждением стенки пищевода и возникновением медиастинита [38,49].
- Бужирование пищевода рекомендуется проводить на фоне продолжающегося (до трех месяцев после ожога) применения кортикостероидов для системного действия, и при наличии возможности, проведения гипербарической оксигенации [23,38,49,61,63].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций B (уровень достоверности доказательств – 3
- Пациентам с послеожоговыми рубцовыми стриктурами пищевода применение методики бужирования «вслепую» не рекомендуется из-за высокого риска перфорации органа [23,38,49,55].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций C (уровень достоверности доказательств – 4)
Комментарий: При бужировании пищевода «вслепую» перфораций пищевода встречаются в 2,5% случаев. Бужирование по нити (антеградно или ретроградно через гастростому), более безопасно, но недостаточно эффективно и переносится пациентами тяжело [23,38,49].
- Пациентам с послеожоговыми рубцовыми стриктурами рекомендуется бужирование пищевода по металлической струне-проводнику с пружинным направителем, под контролем эзофагоскопии или рентгеноскопии [38,49,54,58].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций C (уровень достоверности доказательств – 4)
Комментарий: Показания
1) сужение просвет пищевода менее 9 мм в диаметре;
2) нарушение трофического статуса пациента.
Противопоказания
1) облитерация просвета пищевода;
2) наличие протяжённых стриктур с извилистым ходом, не позволяющим провести струну-проводник. В таких случаях показано наложение гастростомы, при скомпрометированном желудке – еюностомы.
Инструменты
- Стальные направляющие струны (проводники) различной жесткости, длиной 200 или 250 см, снабженные на конце мягким пружинным наконечником.
- Набор полых бужей диаметром от 4,5 до 13 мм (от 14 до 40Fr) с внутренним каналом для направляющей струны длиной 70-80 см.
Сеансы бужирования повторяются через день, основной курс лечения в среднем состоит из 4-5 сеансов.
Бужирование стенозов пищевода, как правило, завершается бужами 42-45Fr (14-16 мм), реже (при коротких, эластичных стриктурах) – 48-51Fr (16-17 мм). При выраженном сопротивлении тканей вмешательство заканчивается бужом, который удается провести без чрезмерных усилий [57].
- Пациентам с формирующимися после химического ожога пищевода рубцовыми стриктурами проведение баллонной дилатации без струны-направителя не рекомендуется из-за высокого риска перфорации [7, 48].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций C (уровень достоверности доказательств – 4)
Комментарий: Для проведения курса лечения в стадии формирования рубцовых тканей необходимо 5-6 сеансов, для чего используют дорогостоящие одноразовые дилататоры. Эффективность баллонной дилатации не выше, чем при бужировании пищевода. В то же время использование баллонной дилатации требует тщательного контроля и больших эндоскопических навыков, и опыта, чем бужирование [7, 11, 23,30,47,56].
- Пациентам с формирующимися после химического ожога рубцовыми стриктурами стентирование пищевода не рекомендуется в качестве метода выбора, но может быть применено как альтернативное лечение [23,64,79-81].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций В (уровень достоверности доказательств – 2)
Комментарий: На сегодняшний день используются металлические (нитиноловые) стенты, рассасывающиеся стенты из полидиоксанона и стенты из силикона. Однако стентирование может сопровождаться такими осложнениями, как грануляционный стеноз, стриктура выше и/или ниже стента, обтурация пищевыми массами, отслойка его внутреннего покрытия с перекрытием просвета, фрагментация и миграция стента, врастание протеза в стенку пищевода с последующим некрозом, образование пролежней и свищей при длительном стентировании, небезопасность удаления, общая доля которых может доходить до 30%. Продолжительность экспозиции не должна превышать двух месяцев, после чего стент следует удалить [64,79-81].
Применение саморасширяющихся биодеградируемых пищеводных стентов из монофиламентной нити полидиоксанона не требует их извлечения, исключает возможность миграции, снижает число осложнений, но позволяет сохранить каркасное и дилатационное действие также только до 2 месяцев [82].
3.3. Лечение в стадии сформированных рубцовых стриктур
- При сформировавшихся коротких стриктура пищевода, вызывающих нарушение проходимости и не обеспечивающих нормальное питания, рекомендуется проводить поддерживающее бужирование в течение первых двух лет после ожога [49,60].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 4)
Комментарий: При сформированном рубце бужирование проводят в амбулаторном режиме 1 раз в неделю, пока при очередном визите не будет отмечено отсутствие значимого рестеноза (просвет пищевода не менее 9 мм) и будет сохранён обычный режим питания. Следующий интервал между сеансами бужирования составляет 2 недели и при сохранении эффекта увеличивается до 3 недель, и затем до 1 месяца. Отсутствие рестеноза в течение месяца, отмеченное трижды, позволяет перейти на профилактическое бужирование через 2, 3, 6 месяцев. В последующем бужирование следует проводить 1-2 раза в год. Неэффективность бужирования с быстрыми рецидивами нарушения проходимости служит показанием к эзофагопластике.
- Временное эндопротезирование пищевода у пациентов в стадии сформированных рубцовых стриктур с использованием трубчатых пластиковых стентов применять не рекомендуется [23,49].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций С (уровень достоверности доказательств – 4)
Комментарии: Стент может вызвать ишемию уже скомпрометированных тканей, что приведет к увеличению протяженности и плотности стриктуры. Допустимо выполнять стентирование при резистентности сужения к традиционным методам дилатации на короткий срок, не превышающий 4-6 недель с эндоскопическим контролем каждые 2 недели и своевременным, а при необходимости и досрочным извлечением стента.
По сводным данным проспективных и ретроспективных мультицентровых исследований, клинический успех стентирования составляет менее 50%, общая частота осложнений – 30%, из них серьёзных – 15%, частота осложнений при извлечении стентов – 10%. Следует избегать использования частично покрытых стентов, непокрытые стенты недопустимы.
Эффективность использования саморассасывающихся (биодеградирующих) стентов с целью длительной поддерживающей дилатация просвета пищевода у данной категории пациентов не имеет доказательной базы.
Стентирование любым саморасправляющимся стентом можно применять в целях предоперационной подготовка у пациентов, которым заведомо показана эзофагопластика [23,49].
3.2.1. Хирургические лечение пациентов с послеожоговыми стриктурами пищевода
- Хирургические лечение пациентов с послеожоговыми стриктурами пищевода рекомендовано в следующих случаях:
1) полная облитерация просвета пищевода;
2) наличие извилистого просвета одной или нескольких стриктур с супрастенотическими расширениями, слепыми карманами и дивертикулами;
3) невозможность провести бужи № 28-30 (по шкале Шарьера) из-за плотных, рецидивирующих стриктур;
4) послеожоговые стриктуры, осложнённые пищеводными свищами;
5) наличие в анамнезе перфорации пищевода;
6) длительное (более 15 лет) существование рубцовых тканей с большим риском их малигнизации;
7) послеожоговое укорочение пищевода с развитием вторичной кардиальной грыжи пищеводного отверстия диафрагмы и рефлюкс-эзофагита [17,33-37,39].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций C (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
Выбор метода
- Циркулярные резекции коротких (до 5 см) стриктур пищевода с анастомозом конец-в конец или замещение резецированного отрезка тонкой кишкой на сосудистой ножке не рекомендуются ввиду высокого риска развития несостоятельности швов [17,31,33-37,39].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций C (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
Комментарии: Кроме того, короткие стриктуры подвергаются бужированию с хорошим результатом.
- При наличии показаний к хирургическому лечению пациентов с послеожоговыми стриктурами рекомендуется создание искусственного пищевода в сочетании с одномоментной резекцией скомпрометированного естественного пищевода, или эти вмешательства выполняют раздельно [17,33-37,39].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций C (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
Комментарии: Выбор метода вмешательства и его объёма зависит от общего состояния пациента, протяжённости рубцовых изменений (вход в пищевод, желудок). В зависимости от этих факторов, хирургическое вмешательство может быть выполнено в один или в несколько этапов. Ключевые вопросы реконструктивной хирургии пищевода - вариант эзофагопластики (заместительная, шунтирующая, отсроченная), пластический материал (желудок, толстая кишка), доступ (трансхиатальный, трансторакальный), способ размещения трансплантата (заднемедиастенальный, ретростернальный) являются прерогативой врачей-хирургов специализированных центров [17,31,33-37,39].
Выбор расположения трансплантата
- Пациентам с длительно существующими рубцовыми стриктурами пищевода с высокой вероятностью малигнизации, наличием пищеводных свищей и при неэффективности бужирования рекомендуется экстирпация пищевода с одномоментной пластикой желудочным или толстокишечным трансплантатом, проведённым в заднем средостении, в ложе удаленного естественного пищевода [17,31,33-37,39].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций C (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
Комментарии: При сохраненном пищеводе лучшие функциональные результаты достигаются при загрудинном расположении трансплантата из толстой кишки (отсутствие желудочно-глоточного рефлюкса, возможность повторной операции на трансплантате в случае его частичного некроза, непроходимости, малигнизации). Если пищевод был удалён ранее, трансплантат также располагают загрудинно, используя толстую кишку [17,33-37,39].
- У пациентов при протяженных послеожоговых рубцовых стриктурах пищевода, не поддающихся бужированию, при условии, что в желудке нет последствий химического ожога рекомендуется выполнение резекции пищевода абдоминоцервикальным доступом с одномоментной эзофагопластикой желудком [17,33-37,39].
Уровень убедительности рекомендаций C (уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
4. Медицинская реабилитация, медицинские показания и противопоказания к применению методов реабилитации
- Медицинскую реабилитацию пациентам после ХОП рекомендуется начинать максимально рано и проводить одновременно с лечением [11,18,23].
Уровень убедительности рекомендации С (Уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
Комментарий. Следует иметь в виду, что на эффективность и сроки физической реабилитации влияет вид химического вещества, степень и распространенность поражения, а также своевременность и полнота оказания неотложной медицинской помощи. Практически все пациенты с ожогами I и IIA степени (по эндоскопической классификации Zargar) выздоравливают без последствий. У большинства пациентов с ожогами IIB степени и у всех выживших с повреждениями III-IV степени развивается рубцевание пищевода или желудка. Ранние серьезные осложнения и смерть наблюдаются, как правило, у пациентов с ожогами III-IV степени [11,18,23].
- Пациентов с ХОП I степени рекомендуется сразу же кормить и выписать из медицинской организации через 24-48 ч [23].
Уровень убедительности рекомендации С (Уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
Комментарий. Этим пациентам не требуется длительного наблюдения, так как риск образования стриктуры равен нулю [23].
- Пациентам, принявшим ВПД с суицидальной целью, рекомендуется психиатрическое обследование (консультация врача-психотерапевта) перед выпиской из медицинской организации [18,23,70,91].
Уровень убедительности рекомендации С (Уровень достоверности доказательств – 4)
Комментарий. Контроль психического состояния и психологическая поддержка обязательны перед выпиской из медицинской организации, независимо от степени тяжести коррозионных повреждений [18]. Во избежание рецидива суицидальной попытки целесообразно долгосрочное наблюдение у врача-психотерапевта [23,70].
5. Профилактика и диспансерное наблюдение, медицинские показания и противопоказания к применению методов профилактики
Прогноз у пациентов с послеожоговыми рубцовыми стриктурами в целом благоприятный при лечебной тактике, адекватной стадии патологического процесса, и при условии диспансерного наблюдения.
Программы общественного здравоохранения по просвещению населения и принятию эффективных мер по ограничению доступа к сильным коррозионным агентам имеют первостепенное значение для снижения частоты и серьезности проглатывания едких веществ. Профилактические стратегии, такие как введение защитных крышек бутылок, использование кристаллических, а не жидких форм коррозионных агентов, надлежащая маркировка и упаковка, а также широкое освещение в средствах массовой информации, доказали свою эффективность в нескольких странах [23].
- Пациентам с ХОП после выписки из стационара рекомендуется диспансерное наблюдение у врача-хирурга поликлиники по месту жительства [23].
Уровень убедительности рекомендации С (Уровень достоверности доказательств – 5)
Комментарий. Для раннего выявления и своевременного лечения таких осложнений, как стриктура пищевода, рекомендуется регулярное наблюдение, частота амбулаторных посещений и лучший способ (клиническое обследование, эндоскопия) для последующего наблюдения все еще остаются предметом обсуждения. Посещение врача-хирурга через 4–6 месяцев после приема внутрь ВПД рекомендуется для пациентов с КТ-признаками II степени, так как большинство стриктур пищевода развиваются в течение этого времени [23,25,26].
Эндоскопия является основным методом диагностики стриктур пищевода / желудка у пациентов, перенесших ХОП. Формирование стриктуры – наиболее частое и приводящее к инвалидности долгосрочное осложнение при проглатывании коррозионных веществ. Стриктуры чаще поражают пищевод, чем желудок, и обычно возникают в течение 4 месяцев после приема внутрь ВПД [25, 26]. Дисфагия и срыгивание являются основными симптомами коррозионных стриктур и требуют немедленного обследования верхних отделов желудочно-кишечного тракта [29].
6. Организация оказания медицинской помощи
Показания для госпитализации в медицинскую организацию:
1). клинико-анамнестические признаки химического ожога пищевода.
Показания к выписке пациента из медицинской организации:
1). отсутствие признаков гнойно-воспалительных осложнений органов средостения и брюшной полости;
2). возможность энтерального питания;
3). стабилизация состояния – адекватное функционирование жизнеобеспечивающих систем организма.
7. Дополнительная информация (в том числе факторы, влияющие на исход заболевания или состояния)
На догоспитальном этапе крайне важно подтвердить проглатывание ВПД и идентифицировать химический агент, оценить причины (случайно или преднамеренно) и время от проглатывания, выявить одновременное употребление алкоголя, и уточнить дополнительные факторы риска (беременность, сопутствующие соматические заболевания) [11,13,18,72].
Следует избегать действий, которые могут вызвать повторное прохождение через пищевод ВПД или привести к аспирации химического агента (положения пациента лежа на спине, промывания желудка, приема разбавителей), а также попыток нейтрализации pH желудочного содержимого, поскольку они могут усугубить травму.
Неотложная помощь при проглатывании ВПД, как и лечение поздних осложнений требует мультидисциплинарного подхода. Рекомендуется ранний контакт с токсикологическим центром [11,13,18,72].
Экстренное КТ-исследование более надежно при оценке трансмурального некроза пищевода при химическом ожоге, чем эндоскопия и улучшает отбор пациентов для неотложной операции.
Хирургическая резекция органов, подверженных трансмуральному некрозу, может спасти жизнь пациенту и должна выполняться в хирургических стационарах первого уровня.
В условиях ограниченных ресурсов предпочтительны простые решения, такие как установка гастростомы или еюностомы, которые могут спасти жизнь, решая жизненно важные проблемы с питанием. Сложные эндоскопические или хирургические процедуры в таких условиях следует проводить осторожно [23,83].
Лечение поздних последствий ХОП в основном основывается на бужировании, эндоскопии (дилатация, стентирование) или сложных хирургических реконструктивных вмешательствах и должно проводиться в специализированных центрах [23].
Критерии оценки качества медицинской помощи
|
№ |
Критерии качества |
Оценка выполнения |
|
|
При отравлении уксусной кислотой определено наличие и уровень свободного гемоглобина в крови и моче |
да/нет |
|
|
Выполнена обзорная рентгенография органов грудной клетки и брюшной полости |
да/нет |
|
|
Выполнена эзофагогастродуоденоскопия (ЭГДС) в первые 48 часов после травмы |
да/нет |
|
|
Выполнена экстренная КТ органов грудной полости с внутривенным контрастированием в острую стадию отравления ВПД (при технической возможности и отсутствии противопоказаний) |
да/нет |
|
|
Проведена комплексная терапия отравления ВПД, включающая удаление токсиканта из ЖКТ, местное лечение и детоксикацию. |
да/нет |
|
|
Выполнена экстренная операция при клинических и рентгенологических признаках перфорации пищевода и/или желудка. |
да/нет |
|
|
При формировании рубцовой стриктуры проведено бужирование пищевода. |
да/нет |
Список литературы
1. Spechler S, Taylor M. Caustic ingestions. In: Taylor MB, editor. Gastrointestinal emergencies. 2nd edition. Baltimore (MD): Lipincott, Williams & Wilkins; 1997. p. 19-31.
2. «Медицинская токсикология» Национальное руководство под редакцией акад. РАМН Е.А. Лужникова. Москва. Издательство: группа ГЭОТАР - Медиа, 2012 – С.638-657.
3. Белькова Т. Ю. Современные принципы диагностики, комплексного лечения химических ожогов пищевода и желудка (сообщение 2) // Сиб. мед. журн. (Иркутск). 2001. №5.
4. Chirica M. et al. Esophageal emergencies: WSES guidelines. World J Emerg Surg. 2019 May 31;14:26. doi: 10.1186/s13017-019-0245-2.
5. Дробязгин Е. А., Чикинев Ю. В., Судовых И. Е. Рак пищевода после химического ожога. Хирургия. Журнал им. Н.И. Пирогова. 2019;(1):27-31. https://doi.org/10.17116/hirurgia201901127.
6. Rafeey M, Ghojazadeh M, Sheikhi S, Vahedi L. Caustic Ingestion in Children: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Caring Sci. 2016 Sep 1;5(3):251-265. doi: 10.15171/jcs.2016.027. PMID: 27757390; PMCID: PMC5045959.
7. Песня-Прасолова Е.А., Ильяшенко К.К., Пинчук Т.П., Гуляев А.А. Комплексная оценка повреждений пищевода и желудка при острых отравлениях прижигающими жидкостями // Клинические перспективы гастроэнтерологии, гепатологии – 2006. - №5. – С. 32–35.
8. Hendrix, I. Emergency oesophageal stripping an aggressive approch to acute necrotic caustic burns of the oesophagus and stomach / I. Hendrix, A. Hubens, W. Van Нее // Acta. chir. belg. - 1990.- Vol. 90.- № 2.- P. 46–49.
9. Bonnici KS, Wood DM, Dargan PI. Should computerised tomography replace endoscopy in the evaluation of symptomatic ingestion of corrosive substances? Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2014 Nov; 52 (9):911-25. doi: 10.3109/15563650.2014.957310.
10. Bahrami-Motlagh H, Hadizadeh-Neisanghalb M, Peyvandi H. Diagnostic Accuracy of Computed Tomography Scan in Detection of Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Injuries Following Caustic Ingestion. Emerg (Tehran). 2017;5(1):e61. Epub 2017 Mar 10. PMID: 28894776; PMCID: PMC5585831.
11. Contini S, Scarpignato C. Caustic injury of the upper gastrointestinal tract: a comprehensive review. World J Gastroenterol. 2013;19 (25):3918–30.
12. Bird JH, Kumar S, Paul C, Ramsden JD. Controversies in the management of caustic ingestion injury: an evidence-based review. Clin Otolaryngol. 2017 Jun;42(3):701-708. doi: 10.1111/coa.12819. Epub 2017 Jan 24. PMID: 28032947.
13. Keh SM, Onyekwelu N, McManus K, et al. Corrosive injury to upper gastrointestinal tract: still a major surgical dilemma. World J Gastroenterol. 2006;12(32):5223–8.
14. Betalli P, Falchetti D, Giuliani S, et al. Caustic ingestion in children: is endoscopy always indicated? The results of an Italian multicenter observational study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2008;68(3):434–9.
15. Temiz A, Oguzkurt P, Ezer SS, et al. Predictability of outcome of caustic ingestion by esophagogastroduodenoscopy in children. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18(10):1098–103.
16. Arici MA, Ozdemir D, Oray NC, et al. Evaluation of caustics and household detergents exposures in an emergency service. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2012;31(6):533–8.
17. Chirica M, Resche-Rigon M, Bongrand NM, et al. Surgery for caustic injuries of the upper gastrointestinal tract. Ann Surg. 2012;256(6):994–1001.
18. Bonavina L, Chirica M, Skrobic O, et al. Foregut caustic injuries: results of the world society of emergency surgery consensus conference. World J Emerg Surg. 2015;10:44.
19. Zerbib P, Voisin B, Truant S, et al. The conservative management of severe caustic gastric injuries. Ann Surg. 2011;253(4):684–8.
20. Chirica M, Resche-Rigon M, Pariente B, et al. Computed tomography evaluation of high-grade esophageal necrosis after corrosive ingestion to avoid unnecessary esophagectomy. Surg Endosc. 2015;29(6):1452–61.
21. Chou SH, Chang YT, Li HP, et al. Factors predicting the hospital mortality of patients with corrosive gastrointestinal injuries receiving esophagogastrectomy in the acute stage. World J Surg. 2010;34(10):2383–8.
22. Chirica M, Resche-Rigon M, Zagdanski AM, Bruzzi M, Bouda D, Roland E, Sabatier F, Bouhidel F, Bonnet F, Munoz-Bongrand N, Marc Gornet J, Sarfati E, Cattan P. Computed Tomography Evaluation of Esophagogastric Necrosis After Caustic Ingestion. Ann Surg. 2016;264(1):107–13.
23. Chirica M., Bonavina L., Kelly M. et al. Caustic ingestion. Lancet 2017 May 20;389(10083):2041-2052. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30313-0.
24. Орлов Ю.П., Орлова Н.В., Михеев Е.Ю., Бенескриптов И.С. Отравления уксусной кислотой. Новый взгляд на старую проблему "русской болезни" // Методическое пособие для врачей. Омск: Тактик-Студио, 2015. - 175 с.
25. Bruzzi M, Chirica M, Resche-Rigon M, et al. Emergency computed tomography predicts caustic esophageal stricture formation. Ann Surg. 2018. https://doi. org/10.1097/SLA.0000000000002732.
26. Cheng HT, Cheng CL, Lin CH, et al. Caustic ingestion in adults: the role of endoscopic classification in predicting outcome. BMC Gastroenterol. 2008; 8:31.
27. Zargar SA, Kochhar R, Mehta S, et al. The role of fiberoptic endoscopy in themanagement of corrosive ingestion and modified endoscopic classification of burns. Gastrointest Endosc. 1991; 37 (2):165–9.
28. Le Naoures P, Hamy A, Lerolle N, et al. Risk factors for symptomatic esophageal stricture after caustic ingestion-a retrospective cohort study. Dis Esophagus. 2017; 30 (6):1–6.
29. Cowan T, Foster R, Isbister GK. Acute esophageal injury and strictures following corrosive ingestions in a 27 year cohort. Am J Emerg Med. 2017; 35 (3):488–92.
30. Lahoti D, Broor SL, Basu PP, et al. Corrosive esophageal strictures: predictors of response to endoscopic dilation. Gastrointest Endosc. 1995;41(3):196–200.
31. Chirica M, Veyrie N, Munoz-Bongrand N, et al. Late morbidity after colon interposition for corrosive esophageal injury: risk factors, management, and outcome. A 20-years experience. Ann Surg. 2010;252(2):271–80.
32. Andreoni B, Farina ML, Biffi R, et al. Esophageal perforation and caustic injury: emergency management of caustic ingestion. Dis Esophagus. 1997;10(2):95–100.
33. Estrera A, Taylor W, Mills LJ, et al. Corrosive burns of the esophagus and stomach: a recommendation for an aggressive surgical approach. Ann Thorac Surg. 1986;41(3):276–83.
34. Di Saverio S, Biscardi A, Piccinini A, et al. Different possible surgical managements of caustic ingestion: diagnostic laparoscopy for Zargar’s grade 3a lesions and a new technique of “duodenal damage control” with “4-tubes ostomy" and duodenal wash-out as an option for extensive 3b lesions in unstable patients. Updat Surg 2015; 67(3):313–320.
35. Dapri G, Himpens J, Mouchart A, et al. Laparoscopic transhiatal esophago- gastrectomy after corrosive injury. Surg Endosc. 2007;21(12):2322–5.
36. Cattan P, Munoz-Bongrand N, Berney T, et al. Extensive abdominal surgery after caustic ingestion. Ann Surg. 2000;231(4):519–23.
37. Chirica M, Kraemer A, Petrascu E, Vuarnesson H, Pariente B, Halimi B, Munoz- Bongrand N, Sarfati E, Cattan P. Esophagojejunostomy after total gastrectomy for caustic injuries. Dis Esophagus. 2014;27(2):122–7.
38. Галлингер Ю.И., Годжелло Э.А. Эндоскопическое лечение рубцовых стенозов пищевода. Эндоскоп хир 2000; 5: 33—39.
39. Lefrancois M, Gaujoux S, Resche-Rigon M, et al. Oesophagogastrectomy and pancreatoduodenectomy for caustic injury. Br J Surg. 2011;98(7):983–90.
40. Benjamin B, Agueb R, Vuarnesson H, Tranchart H, Bongrand NM, Sarfati E, Cattan P, Chirica M. Tracheobronchial Necrosis After Caustic Ingestion. Ann Surg. 2016;263(4):808–13.
41. De Lusong MAA, Timbol ABG, Tuazon DJS. Management of esophageal caustic injury. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. 2017 May 6;8(2):90-98. doi: 10.4292/wjgpt.v8.i2.90.
42. Havanond C, Havanond P. Initial signs and symptoms as prognostic indicators of severe gastrointestinal tract injury due to corrosive ingestion. J Emerg Med 2007; 33: 349-353 [PMID: 17976790 DOI: 10.1016/j.jemermed.2007.02.062.
43. Le Naoures P, Hamy A, Lerolle N, et al. Risk factors for symptomatic esophageal stricture after caustic ingestion-a retrospective cohort study. Dis Esophagus. 2017;30(6):1 – 6.
44. Tiryaki T, Livanelioğlu Z, Atayurt H. Early bougienage for relief of stricture formation following caustic esophageal burns. Pediatr Surg Int 2005; 21: 78-80.
45. Park KS. Evaluation and management of caustic injuries from ingestion of Acid or alkaline substances. Clin Endosc 2014; 47: 301-307 [PMID: 25133115 DOI: 10.5946/ce.2014.47.4.301.
46. Methasate A, Lohsiriwat V. Role of endoscopy in caustic injury of the esophagus. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2018 Oct 16;10(10):274-282. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v10.i10.274.PMID: 30364838.
47. Sami SS, Haboubi HN, Ang Y, Boger P, Bhandari P, de Caestecker J, Griffiths H, Haidry R, Laasch HU, Patel P, Paterson S, Ragunath K, Watson P, Siersema PD, Attwood SE. UK guidelines on oesophageal dilatation in clinical practice. Gut. 2018 Jun;67(6):1000-1023.
48. Luedtke P, Levine MS, Rubesin SE, Weinstein DS, Laufer I. Radiologic diagnosis of benign esophageal strictures: a pattern approach. Radiographics. 2003 Jul-Aug;23(4):897-909.
49. Годжелло Э. А., Галлингер Ю. И., Хрусталева М. В., Евдокимова Е. В., Ходаковская Ю. А. Современная концепция эндоскопического лечения рубцовых стриктур пищевода и пищеводных анастомозов. Хирургия. Журнал им. Н.И. Пирогова. 2013;(2):97-104.
50. Chiu HM, Lin JT, Huang SP, Chen CH, Yang CS, Wang HP. Prediction of bleeding and stricture formation after corrosive ingestion by EUS concurrent with upper endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc 2004; 60: 827-833 [PMID: 15557970].
51. Kamijo Y, Kondo I, Kokuto M, Kataoka Y, Soma K. Miniprobe ultrasonography for determining prognosis in corrosive esophagitis. Am J Gastroenterol 2004; 99: 851-854 [PMID: 15128349].
52. Rana SS, Sharma R, Gupta R. High-frequency miniprobe endoscopic ultrasonography for evaluation of indeterminate esophageal strictures. Ann Gastroenterol. 2018 Nov-Dec;31(6):680-684.
53. Ghiselli A. Bizzarri В. Ferrari D. et al. Endoscopic dilation in pediatric esophageal strictures: a literature review. Acta Biomed. 2018; 89(Suppl 8): 27–32. doi: 10.23750/abm.v89i8-S.7862.
54. Siersema PD, de Wijkerslooth LR. Dilation of refractory benign esophageal strictures. Gastrointest Endosc 2009; 70: 1000–12.
55. Tulman AB, Boyce HW. Complications of esophageal dilation and guidelines for their prevention. Gastrointest Endosc. 1981 Nov;27(4):229-34.
56. Ravich WJ. Endoscopic Management of Benign Esophageal Strictures. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2017 Aug 24;19(10):50. doi: 10.1007/s11894-017-0591-8.
57. Raymondi R, Pereira-Lima JC, Valves A, Morales GF, Marques D, Lopes CV, Marroni CA. Endoscopic dilation of benign esophageal strictures without fluoroscopy: experience of 2750 procedures. Hepatogastroenterology. 2008 Jul-Aug;55(85):1342-8.
58. Pereira-Lima JC, Ramires RP, Zamin I, Cassal AP, Marroni CA, Mattos AA. Endoscopic dilation of benign esophageal strictures: report on 1043 procedures. Am J Gastroenterol. 1999 Jun;94(6):1497-501.
59. Chiu Yi-Chun, Liang Chih-Ming, Tam William et al. The effects of endoscopic-guided balloon dilations in esophageal and gastric strictures caused by corrosive injuries.BMC Gastroenterology volume 13, Article number: 99 (2013).
60. Vermeulen BD, de Zwart M, Sijben J, et al. Risk factors and clinical outcomes of endoscopic dilation in benign esophageal strictures: a long-term follow-up study. Gastrointest Endosc 2020; 91:1058–1066.
61. Poincloux L, Rouquette O, Abergel A. Endoscopic treatment of benign esophageal strictures: a literature review. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2016; 11:53–64.
62. Abad MRA, Yusuke Fujiyoshi Y, Inoue Н. Flexible endoscopic strategies for the difficult esophageal stricture Curr Opin Gastroenterol . 2020 Sep;36(5):379-384.
63. Nijhawan S, Udawat HP, Nagar P. Aggressive bougie dilatation and intralesional steroids is effective in refractory benign esophageal strictures secondary to corrosive ingestion. Dis Esophagus 2016; 29: 1027-1031
64. Spaander M.C.W., Baron T.H., Siersema P.D. et al. Esophageal stenting for benign and malignant disease: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Clinical Guideline. Endoscopy. 2016 Oct;48(10):939-48. doi: 10.1055/s-0042-114210. Epub 2016 Sep 14.
65. Sarioglu-Buke A, Corduk N, Atesci F, Karabul M, Koltuksuz U. A different aspect of corrosive ingestion in children: socio-demographic characteristics and effect of family functioning. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2006; 70: 1791-1798 [PMID: 16839614].
66. Gumaste VV, Dave PB. Ingestion of corrosive substances by adults. Am J Gastroenterol 1992; 87: 1-5 [PMID: 1728104]
67. Balderas A.B., Aceves M.R., Ramírez P.C. Endoscopic findings of the digestive tract secondary to causticingestion in children seen at the Emergency Department Arch Argent Pediatr 2018;116(6):409-414.
68. Mamede RC, de Mello Filho FV. Ingestion of caustic substances and its complications. Sao Paulo Med J 2001; 119: 10-15 [PMID: 11175619]
69. Osman M, Russell J, Shukla D, Moghadamfalahi M, Granger DN. Responses of the murine esophageal microcirculation to acute exposure to alkali, acid, or hypochlorite. J Pediatr Surg 2008; 43: 1672-1678 [PMID: 18779005].
70. Christesen H. B. Caustic ingestion in adults--epidemiology and prevention. J Toxicol Clin. Toxicol1994;32(5):557-68. doi: 10.3109/15563659409011060.
71. Arévalo-Silva C, Eliashar R, Wohlgelernter J, Elidan J, Gross M. Ingestion of caustic substances: a 15-year experience. Laryngoscope 2006; 116: 1422-1426 [PMID: 16885747 DOI: 10.1097/01.mlg.0000225376.83670.4d].
72. Ramasamy K, Gumaste VV. Corrosive ingestion in adults. J Clin Gastroenterol 2003; 37: 119-124.
73. Skucas J. Contrast media. In: Gore R, Levine M, Laufer I. Textbook of Gastrointestinal Radiology. Philadelphia: WB Saunders, 2000: 2-14.
74. Contini S, Tesfaye M, Picone P, Pacchione D, Kuppers B, Zambianchi C, Scarpignato C. Corrosive esophageal injuries in children. A shortlived experience in Sierra Leone. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2007; 71: 1597-1604 [PMID: 17716749].
75. Baskin D, Urganci N, Abbasoğlu L, Alkim C, Yalçin M, Karadağ C, Sever N. A standardised protocol for the acute management of corrosive ingestion in children. Pediatr Surg Int 2004; 20: 824-828.
76. Рoley JW, Steyerberg EW, Kuipers EJ, Dees J, Hartmans R, Tilanus HW, Siersema PD. Ingestion of acid and alkaline agents: outcome and prognostic value of early upper endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc 2004; 60: 372-377.
77. Previtera C, Giusti F, Guglielmi M. Predictive value of visible lesions (cheeks, lips, oropharynx) in suspected caustic ingestion: may endoscopy reasonably be omitted in completely negative pediatric patients? Pediatr Emerg Care 1990; 6: 176-178 [PMID: 2216918].
78. Ananthakrishan N., Parthasarathy G., Kate V. Acute corrosive injuries of the stomach: a single unit experience of thirty years. ISRN Gastroenterol 2011; 2011:914013[PMID:21991535 DOI:10.5402/2011/914013].
79. Tandon S, Burnand KM, De Coppi P, McLaren CA, Roebuck DJ, Curry JI. Self-expanding esophageal stents for the management of benign refractory esophageal strictures in children: A systematic review and review of outcomes at a single center. J Pediatr Surg. 2019 Dec;54(12):2479-2486. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2019.08.041.
80. Fuccio L, Hassan C, Frazzoni L, Miglio R, Repici A. Clinical outcomes following stent placement in refractory benign esophageal stricture: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Endoscopy. 2016 Feb;48(2):141-8. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1393331.
81. Thomas T, Abrams KR, Subramanian V, Mannath J, Ragunath K. Esophageal stents for benign refractory strictures: a meta-analysis. Endoscopy. 2011 May;43(5):386-93. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1256331.
82. Imaz-Iglesia I, García-Pérez S, Nachtnebel A, Martín-Águeda B, Sánchez-Piedra C, Karadayi B, Demirbaş AR. Biodegradable stents for the treatment of refractory or recurrent benign esophageal stenosis. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2016 Jun;13(6):583-99. doi: 10.1080/17434440.2016.1184967.
83. Contini S, Swarray-Deen A, Scarpignato C. Oesophageal corrosive injuries in children: a forgotten social and health challenge in developing countries.Bull World Health Organ, 87 (2009), pp. 950-954.
84. Rigo G. P. et al. What is the utility of selected clinical and endoscopic parameters in predicting the risk of death after caustic ingestion? //Endoscopy. – 2002. – Т. 34. – №. 04. – С. 304-310.
85. Otçu S. et al. Biochemical indicators of caustic ingestion and/or accompanying esophageal injury in children //Turkish journal of pediatrics. – 2003. – Т. 45. – №. 1. – С. 21-25.
86. Cheng Y. J., Kao E. L. Arterial blood gas analysis in acute caustic ingestion injuries //Surgery today. – 2003. – Т. 33. – №. 7. – С. 483-485.
87. Демидчик Л. А. и др. Окисленные белки в крови больных с острым отравлением уксусной кислотой //Международный журнал прикладных и фундаментальных исследований. – 2018. – №. 5-1. – С. 82-86.
88. Usta M, Erkan T, Cokugras FC, Urganci N, Onal Z, Gulcan M, Kutlu T. High doses of methylprednisolone in the management of caustic esophageal burns. Pediatrics. 2014 Jun;133(6):E1518-24. doi: 10.1542/peds.2013-3331. PMID: 24864182.
89. Boukthir S, Fetni I, Mrad SM, Mongalgi MA, Debbabi A, Barsaoui S. Corticothérapie à forte dose dans le traitement des oesophagites caustiques sévères chez l"enfant [High doses of steroids in the management of caustic esophageal burns in children]. Arch Pediatr. 2004 Jan;11(1):13-7. French. doi: 10.1016/j.arcped.2003.10.011. PMID: 14700754.
90. Bautista A, Varela R, Villanueva A, Estevez E, Tojo R, Cadranel S. Effects of prednisolone and dexamethasone in children with alkali burns of the oesophagus. Eur J Pediatr Surg. 1996 Aug;6(4):198-203. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1066507. PMID: 8877349.
91. Mamede R. C. M., De Mello Filho F. V. Treatment of caustic ingestion: an analysis of 239 cases //Diseases of the Esophagus. – 2002. – Т. 15. – №. 3. – С. 210-213.
92. King CS, Holley AB, Jackson JL, Shorr AF, Moores LK. Twice vs three times daily heparin dosing for thromboembolism prophylaxis in the general medical population: A metaanalysis. Chest. 2007 Feb;131(2):507-16. doi: 10.1378/chest.06-1861. PMID: 17296655.
Приложение А1. Состав рабочей группы по разработке и пересмотру клинических рекомендаций
Абакумов М.М. – доктор медицинских наук, профессор
Аллахвердян А.С. – доктор медицинских наук, профессор
Годжело Э.А. – доктор медицинских наук, профессор
Даниелян Ш.Н. – доктор медицинских наук
Дробязгин Е.А. – доктор медицинских наук
Жестков К.Г. – доктор медицинских наук, профессор
Ильяшенко К.К. – доктор медицинских наук, профессор
Корымасов Е.А. – доктор медицинских наук, профессор
Лодягин А.Н. – доктор медицинских наук, профессор
Ручкин Д.В. – доктор медицинских наук
Хоробрых Т.В. – доктор медицинских наук, профессор
Черкасов М.Ф. – доктор медицинских наук, профессор
Чикинев Ю.В. – доктор медицинских наук, профессор
Шулутко А.М. – доктор медицинских наук, профессор
Конфликт интересов отсутствует.
Приложение А2. Методология разработки клинических рекомендаций
В данных клинических рекомендациях все сведения ранжированы по уровню достоверности (доказательности) в зависимости от количества и качества исследований по данной проблеме.
Целевая аудитория данных клинических рекомендаций:
- врачи-хирурги
- врачи-торакальные хирурги
- врачи-эндоскописты
- врачи-рентгенологи
- врачи-анестезиологи-реаниматологи
- врачи-токсикологи
- врачи скорой медицинской помощи
- студенты и ординаторы медицинских вузов
Таблица А2.1. Шкала оценки уровней достоверности доказательств (УДД) для методов диагностики (диагностических вмешательств)
|
УДД |
Расшифровка |
|
1. |
Систематические обзоры исследований с контролем референсным методом или систематический обзор рандомизированных клинических исследований с применением мета-анализа |
|
2. |
Отдельные исследования с контролем референсным методом или отдельные рандомизированные клинические исследования и систематические обзоры исследований любого дизайна, за исключением рандомизированных клинических исследований, с применением мета-анализа |
|
3. |
Исследования без последовательного контроля референсным методом или исследования с референсным методом, не являющимся независимым от исследуемого метода или нерандомизированные сравнительные исследования, в том числе когортные исследования |
|
4. |
Несравнительные исследования, описание клинического случая |
|
5. |
Имеется лишь обоснование механизма действия или мнение экспертов |
Таблица А2.2. Шкала оценки уровней достоверности доказательств (УДД) для методов профилактики, лечения и реабилитации (профилактических, лечебных, реабилитационных вмешательств)
|
УДД |
Расшифровка |
|
1. |
Систематический обзор рандомизированных клинических исследований с применением мета-анализа |
|
2. |
Отдельные рандомизированные клинические исследования и систематические обзоры исследований любого дизайна, за исключением рандомизированных клинических исследований, с применением мета-анализа |
|
3. |
Нерандомизированные сравнительные исследования, в том числе когортные исследования |
|
4. |
Несравнительные исследования, описание клинического случая или серии случаев, исследование "случай-контроль" |
|
5. |
Имеется лишь обоснование механизма действия вмешательства (доклинические исследования) или мнение экспертов |
Таблица А.2.3. Шкала оценки уровней убедительности рекомендаций (УУР) для методов профилактики, диагностики, лечения и реабилитации (профилактических, диагностических, лечебных, реабилитационных вмешательств)
|
УУР |
Расшифровка |
|
A |
Сильная рекомендация (все рассматриваемые критерии эффективности (исходы) являются важными, все исследования имеют высокое или удовлетворительное методологическое качество, их выводы по интересующим исходам являются согласованными) |
|
B |
Условная рекомендация (не все рассматриваемые критерии эффективности (исходы) являются важными, не все исследования имеют высокое или удовлетворительное методологическое качество и/или их выводы по интересующим исходам не являются согласованными) |
|
C |
Слабая рекомендация (отсутствие доказательств надлежащего качества (все рассматриваемые критерии эффективности (исходы) являются неважными, все исследования имеют низкое методологическое качество и их выводы по интересующим исходам не являются согласованными) |
Приложение А3. Справочные материалы, включая соответствие показаний к применению и противопоказаний, способов применения и доз лекарственных препаратов, инструкции по применению лекарственного препарата
Определение степени тяжести отравления ВПД по данным лабораторных исследований [2]:
отравление легкой степени: токсическая нефропатия легкой степени: микрогематурия (до 6-10 свежих эритроцитов в поле зрения), умеренная лейкоцитурия, протеинурия (до 6,6 г/л), гемоглобинурия, снижение клубочковой фильтрации, концентрационного индекса, креатинина, уровень остаточного азота и мочевины в пределах нормы;
отравление средней тяжести: гемолиз, гемоглобинурия 5-10г/л, токсическая нефропатия средней степени тяжести (протеинурия, уровень остаточного азота и мочевины в пределах нормы, умеренное повышение креатинина), токсическая гепатопатия легкой или средней степени тяжести (повышение уровня билирубина, аланинаминотрансферазы, аспартатаминотрансферазы, общей активности лактатдегидрогеназы);
- отравление тяжелой степени: гемолиз, гемоглобинурия более 10 г/л, токсическая нефропатия средней или тяжелой степени (удельный вес мочи от 1026 до1042, протеинурия от 6,6 до 33 г/л, гиалиновые и зернистые цилиндры, свежие измененные и выщелоченные эритроциты, большое число лейкоцитов, в крови повышение уровня мочевины, креатинина, калия), тяжелая токсическая гепатопатия (высокий уровень билирубина, аланинаминотрансферазы, аспартатаминотрансферазы, лактатдегидрогеназы), декомпенсированный метаболический ацидоз.
Приложение Б. Алгоритмы действий врача
Приложение В. Информация для пациента
Практически все пациенты с ожогами I и IIA степени выздоравливают без последствий. У большинства пациентов с более тяжелой степенью химического ожога развивается рубцевание пищевода или желудка. Ранние серьезные осложнения и смерть наблюдаются, как правило, у пациентов с ожогами III-IV степени.
Рубцовое сужение чаще происходит в пищеводе, чем в желудке, и обычно возникает в течение 4 месяцев после приема внутрь прижигающего вещества.
После выписки из стационара пациент с диагностированным химическим ожогом пищевода II и выше степени должен посетить врача-хирурга и регулярно наблюдаться у него в течение первых 4–6 месяцев.
На длительный срок назначается щадящая диета № 1. Так как такая диета не может обеспечить повышенную потребность в белках, рацион необходимо дополнять яйцами всмятку, творогом, блюдами из отварного мяса, а также витаминами.
Основным симптомом формирования рубцового сужения пищевода является дисфагия (затруднение при проглатывании пищи). При появлении признаков дисфагии необходимо немедленно обратиться к врачу (врачу-хирургу или врачу-терапевту или врачу-гастроэнтерологу) для проведения обследования верхних отделов желудочно-кишечного тракта.
Эндоскопия является основным методом диагностики послеожогового рубцового сужения пищевода и желудка, но возможно и рентгенологическое исследование.
Приложение Г1-ГN. Шкалы оценки, вопросники и другие оценочные инструменты состояния пациента, приведенные в клинических рекомендациях
.
По теме:
- Статьи: Химические ожоги пищевода: степени, симптомы
- Статьи: ФЕДЕРАЛЬНЫЕ КЛИНИЧЕСКИЕ РЕКОМЕНДАЦИИ «Токсическое действие разъедающих веществ», «Токсическое действие мыл и детергентов» 2014
- Статьи: Классификация Заргар (Zargar classification) - оценка повреждения пищевода при проглатывании едких (каустических) веществ
Рекомендуемые статьи
Ахалазия кардии
Ахалазия кардии (синонимы: мегаэзофагус или долихоэзофагус, идиопатическое расширение пищевода, кардиоспазм и др.)— идиопатическое нервно-мышечное заболевание, проявляющееся функциональным нарушением проходимости кар-дии вследствие дискоординации между глотком, рефлекторным раскрытием нижнего пищеводного сфинктера (НПС) идвигательной итонической активностью гладкой мускулатуры пищевода. Код по МКБ-10К.22.0. Ахалазия кардиальной части.
При эндоскопическом исследовании в случае бронхоэктазов в стадии ремиссии выявляется
частично диффузный бронхит I степени воспаления
Активируйте PUSH уведомления в браузер
Отключите PUSH уведомления в браузер
Содержание
Интернет магазин
Популярное
- О нас
- Правовые вопросы
- Политика
обработки персональных
данных EndoExpert.ru - Связаться с нами
- Стать партнером
© 2016-2022 EndoExpert.ru

Вы находитесь в разделе предназначенном только для специалистов (раздел для пациентов по ссылке). Пожалуйста, внимательно прочитайте полные условия использования и подтвердите, что Вы являетесь медицинским или фармацевтическим работником или студентом медицинского образовательного учреждения и подтверждаете своё понимание и согласие с тем, что применение рецептурных препаратов, обращение за той или иной медицинской услугой, равно как и ее выполнение, использование медицинских изделий, выбор метода профилактики, диагностики, лечения, медицинской реабилитации, равно как и их применение, возможны только после предварительной консультации со специалистом. Мы используем файлы cookie, чтобы предложить Вам лучший опыт взаимодействия. Файлы cookie позволяют адаптировать веб-сайты к вашим интересам и предпочтениям.
Я прочитал и настоящим принимаю вышеизложенное, хочу продолжить ознакомление с размещенной на данном сайте информацией для специалистов.


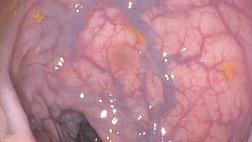




.jpg)

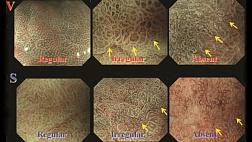
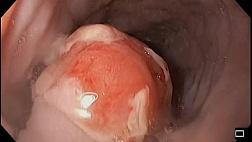
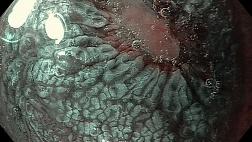

.png)


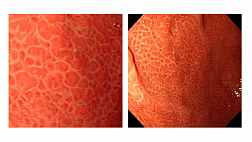














Комментарии